Beneficial effects of a Q-ter based nutritional mixture on functional performance, mitochondrial function, and oxidative stress in rats
- PMID: 20485503
- PMCID: PMC2868025
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010572
Beneficial effects of a Q-ter based nutritional mixture on functional performance, mitochondrial function, and oxidative stress in rats
Abstract
Background: Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are central mechanisms underlying the aging process and the pathogenesis of many age-related diseases. Selected antioxidants and specific combinations of nutritional compounds could target many biochemical pathways that affect both oxidative stress and mitochondrial function and, thereby, preserve or enhance physical performance.
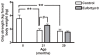
Methodology/principal findings: In this study, we evaluated the potential anti-aging benefits of a Q-ter based nutritional mixture (commercially known as Eufortyn) mainly containing the following compounds: terclatrated coenzyme Q(10) (Q-ter), creatine and a standardized ginseng extract. We found that Eufortyn supplementation significantly ameliorated the age-associated decreases in grip strength and gastrocnemius subsarcolemmal mitochondria Ca(2+) retention capacity when initiated in male Fischer344 x Brown Norway rats at 21 months, but not 29 months, of age. Moreover, the increases in muscle RNA oxidation and subsarcolemmal mitochondrial protein carbonyl levels, as well as the decline of total urine antioxidant power, which develop late in life, were mitigated by Eufortyn supplementation in rats at 29 months of age.
Conclusions/significance: These data imply that Eufortyn is efficacious in reducing oxidative damage, improving the age-related mitochondrial functional decline, and preserving physical performance when initiated in animals at early midlife (21 months). The efficacy varied, however, according to the age at which the supplementation was provided, as initiation in late middle age (29 months) was incapable of restoring grip strength and mitochondrial function. Therefore, the Eufortyn supplementation may be particularly beneficial when initiated prior to major biological and functional declines that appear to occur with advancing age.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
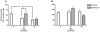
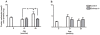
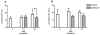
References
-
- Leeuwenburgh C, Prolla TA. Genetics, redox signaling, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in mammalian aging. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:503–505. - PubMed
-
- Muller FL, Lustgarten MS, Jang Y, Richardson A, Van RH. Trends in oxidative aging theories. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43:477–503. - PubMed
-
- Miquel J, Economos AC, Fleming J, Johnson JE., Jr Mitochondrial role in cell aging. Exp Gerontol. 1980;15:575–591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

