Treatment and relapse of autoimmune pancreatitis
- PMID: 20485603
- PMCID: PMC2871571
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2008.2.1.1
Treatment and relapse of autoimmune pancreatitis
Abstract
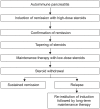
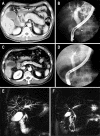
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a peculiar type of chronic pancreatitis whose pathogenesis involves autoimmune mechanisms. The steroid responsiveness has a significant impact on the diagnosis of AIP because patients with AIP and pancreatic cancer share many clinical features. This review focuses on the treatment and relapse of AIP. The goal of AIP treatment is remission of symptoms, serology, radiologic changes, or histology, which also applies to relapse. Although it is generally agreed that steroids should be offered to AIP patients with active disease, there is no standardized steroid regimen for AIP and no consensus on the dose and duration of steroid induction and tapering schedule, and optimal duration and dose of maintenance therapy. Obtaining a consensus on the optimal treatment regimen is very important to reducing the relapse rate. In this review, we discuss the treatment regimens used in many centers.
Keywords: Autoimmune pancreatitis; Relapse; Treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Kim KP, Kim MH, Song MH, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK. Autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1605–1616. - PubMed
-
- Kwon S, Kim MH, Choi EK. The diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis: it is time to make a consensus. Pancreas. 2007;34:279–286. - PubMed
-
- Chari ST, Murray JA. Autoimmune pancreatitis, Part II: the relapse. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:625–628. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Egawa N, Nakajima H, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. Morphological changes after steroid therapy in autoimmune pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:1154–1158. - PubMed
-
- Song MH, Kim MH, Lee SK, et al. Regression of pancreatic fibrosis after steroid therapy in patients with autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2005;30:83–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

