Activity and enantioselectivity of the hydroxynitrile lyase MeHNL in dry organic solvents
- PMID: 20486110
- PMCID: PMC2970910
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201000487
Activity and enantioselectivity of the hydroxynitrile lyase MeHNL in dry organic solvents
Abstract
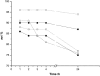
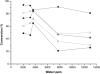
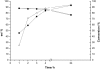
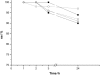
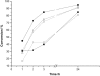
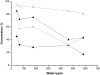
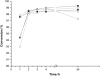
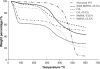
Water concentration affects both the enantioselectivity and activity of enzymes in dry organic media. Its influence has been investigated using the hydrocyanation of benzaldehyde catalyzed by hydroxynitrile lyase cross-linked enzyme aggregate (MeHNL-CLEA) as a model reaction. The enzyme displayed higher enantioselectivity at higher water concentration, thus suggesting a positive effect of enzyme flexibility on selectivity. The activity increased on reducing the solvent water content, but drastic dehydration of the enzyme resulted in a reversible loss of activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure-Based Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Hydroxynitrile Lyase from Cyanogenic Millipede, Oxidus gracilis for Hydrocyanation and Henry Reactions.Chembiochem. 2024 Jun 3;25(11):e202400118. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400118. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 38526556
-
Hydroxynitrile lyase at the diisopropyl ether/water interface: evidence for interfacial enzyme activity.Biotechnol Bioeng. 1999 Nov 20;65(4):425-36. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1999. PMID: 10506418
-
Hydroxynitrile lyase catalysis in ionic liquid-containing systems.Biotechnol Lett. 2005 Sep;27(18):1387-90. doi: 10.1007/s10529-005-0686-4. Biotechnol Lett. 2005. PMID: 16215854
-
Enantioselective synthesis of cyanohydrins catalysed by hydroxynitrile lyases - a review.Org Biomol Chem. 2016 Jul 6;14(27):6375-89. doi: 10.1039/c6ob00934d. Org Biomol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27282284 Review.
-
Immobilisation of hydroxynitrile lyases.Chem Soc Rev. 2013 Aug 7;42(15):6308-21. doi: 10.1039/c3cs35491a. Chem Soc Rev. 2013. PMID: 23361417 Review.
Cited by
-
Continuous Flow Bioamination of Ketones in Organic Solvents at Controlled Water Activity using Immobilized ω-Transaminases.Adv Synth Catal. 2020 Apr 27;362(9):1858-1867. doi: 10.1002/adsc.201901274. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Adv Synth Catal. 2020. PMID: 32421034 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

