Treatment of traumatic brain injury with thymosin β₄ in rats
- PMID: 20486893
- PMCID: PMC2962722
- DOI: 10.3171/2010.4.JNS10118
Treatment of traumatic brain injury with thymosin β₄ in rats
Abstract
Object: This study was designed to investigate the efficacy of delayed thymosin β(4) (Tβ(4)) treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
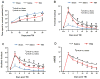
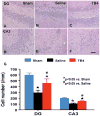
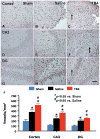
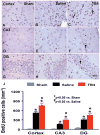
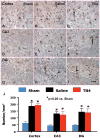
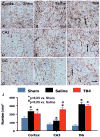
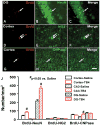
Methods: Young adult male Wistar rats were divided into the following groups: 1) sham group (6 rats); 2) TBI + saline group (9 rats); 3) and TBI + Tβ(4) group (10 rats). Traumatic brain injury was induced by controlled cortical impact over the left parietal cortex. Thymosin β(4) (6 mg/kg) or saline was administered intraperitoneally starting at Day 1 and then every 3 days for an additional 4 doses. Neurological function was assessed using a modified neurological severity score (mNSS), foot fault, and Morris water maze tests. Animals were killed 35 days after injury, and brain sections were stained for immunohistochemistry to assess angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and oligodendrogenesis after Tβ(4) treatment.
Results: Compared with the saline treatment, delayed Tβ(4) treatment did not affect lesion volume but significantly reduced hippocampal cell loss, enhanced angiogenesis and neurogenesis in the injured cortex and hippocampus, increased oligodendrogenesis in the CA3 region, and significantly improved sensorimotor functional recovery and spatial learning.
Conclusions: These data for the first time demonstrate that delayed administration of Tβ(4) significantly improves histological and functional outcomes in rats with TBI, indicating that Tβ(4) has considerable therapeutic potential for patients with TBI.
Figures
References
-
- Barth TM, Jones TA, Schallert T. Functional subdivisions of the rat somatic sensorimotor cortex. Behav Brain Res. 1990;39:73–95. - PubMed
-
- Baskin YK, Dietrich WD, Green EJ. Two effective behavioral tasks for evaluating sensorimotor dysfunction following traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurosci Methods. 2003;129:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Bednarek R, Boncela J, Smolarczyk K, Cierniewska-Cieslak A, Wyroba E, Cierniewski CS. Ku80 as a novel receptor for thymosin beta4 that mediates its intracellular activity different from G-actin sequestering. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:1534–1544. - PubMed
-
- Bock-Marquette I, Saxena A, White MD, Dimaio JM, Srivastava D. Thymosin beta4 activates integrin-linked kinase and promotes cardiac cell migration, survival and cardiac repair. Nature. 2004;432:466–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

