Interaction specificity, toxicity and regulation of a paralogous set of ParE/RelE-family toxin-antitoxin systems
- PMID: 20487277
- PMCID: PMC2907451
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07207.x
Interaction specificity, toxicity and regulation of a paralogous set of ParE/RelE-family toxin-antitoxin systems
Abstract
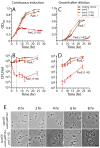
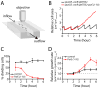
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) gene cassettes are widely distributed across bacteria, archaea and bacteriophage. The chromosome of the alpha-proteobacterium, Caulobacter crescentus, encodes eight ParE/RelE-superfamily toxins that are organized into operons with their cognate antitoxins. A systematic genetic analysis of these parDE and relBE TA operons demonstrates that seven encode functional toxins. The one exception highlights an example of a non-functional toxin pseudogene. Chromosomally encoded ParD and RelB proteins function as antitoxins, inhibiting their adjacently encoded ParE and RelE toxins. However, these antitoxins do not functionally complement each other, even when overexpressed. Transcription of these paralogous TA systems is differentially regulated under distinct environmental conditions. These data support a model in which multiple TA paralogs encoded by a single bacterial chromosome form independent functional units with insulated protein-protein interactions. Further characterization of the parDE(1) system at the single-cell level reveals that ParE(1) toxin functions to inhibit cell division but not cell growth; residues at the C-terminus of ParE(1) are critical for its stability and toxicity. While continuous ParE(1) overexpression results in a substantial loss in cell viability at the population level, a fraction of cells escape toxicity, providing evidence that ParE(1) toxicity is not uniform within clonal cell populations.
Figures
References
-
- Christensen SK, Gerdes K. RelE toxins from bacteria and Archaea cleave mRNAs on translating ribosomes, which are rescued by tmRNA. Mol Microbiol. 2003;48:1389–1400. - PubMed
-
- Christensen SK, Pedersen K, Hansen FG, Gerdes K. Toxin-antitoxin loci as stress-response-elements: ChpAK/MazF and ChpBK cleave translated RNAs and are counteracted by tmRNA. J Mol Biol. 2003;332:809–819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

