The effect of Neuragen PN on neuropathic pain: A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 20487567
- PMCID: PMC2883533
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-10-22
The effect of Neuragen PN on neuropathic pain: A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the naturally derived topical oil, "Neuragen PN" for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
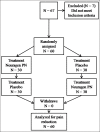
Methods: Sixty participants with plantar cutaneous (foot sole) pain due to all cause peripheral neuropathy were recruited from the community. Each subject was randomly assigned to receive one of two treatments (Neuragen PN or placebo) per week in a crossover design. The primary outcome measure was acute spontaneous pain level as reported on a visual analog scale.
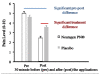
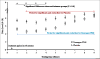
Results: There was an overall pain reduction for both treatments from pre to post application. As compared to the placebo, Neuragen PN led to significantly (p < .05) greater pain reduction. Fifty six of sixty subjects (93.3%) receiving Neuragen PN reported pain reduction within 30 minutes. This reduction within 30 minutes occurred in only twenty one of sixty (35.0%) subjects receiving the placebo. In a break out analysis of the diabetic only subgroup, 94% of subjects in the Neuragen PN group achieved pain reduction within 30 minutes vs 11.0% of the placebo group. No adverse events were observed.
Conclusions: This randomized, placebo controlled, clinical trial with crossover design revealed that the naturally derived oil, Neuragen PN, provided significant relief from neuropathic pain in an all cause neuropathy group. Participants with diabetes within this group experienced similar pain relief.
Trial registration: ISRCTN registered: ISRCTN13226601.
Figures
References
-
- Setacci C, de Donato G, Setacci F, Chisci E. Diabetic patients: epidemiology and the global impact. J Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;50(3):263–273. - PubMed
-
- Argoff CE, Backonja MM, Belgrade MJ, Bennett GJ, Clark MR, Cole BE, Fishbain DA, Irving GA, McCarberg BH, McLean MJ. Consensus guidelines: treatment planning and options. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2006;81(4):S12–S25. - PubMed
-
- Duloxetine: new indication. Depression and diabetic neuropathy: too many adverse effects. Prescrire Int. 2006;15(85):168–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

