A modified formula for calculating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol values
- PMID: 20487572
- PMCID: PMC2890624
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-52
A modified formula for calculating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol values
Abstract
Background: The Friedewald formula (FF) is useful for calculating serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) values, but has a remarkable deviation and limitation especially in hypertriglyceridemia. We modify the formula which is now more suitable for LDL-C calculation.
Methods: 2180 cases were classified into three groups according to their TG concentrations (A: < 200 mg/dl, n = 1220; B: 200-400 mg/dl, n = 480; C: 400-1000 mg/dl, n = 480). The concentrations of LDL-C were measured or estimated by 1) a direct measurement (DM); 2) the FF; and 3) our modified Friedewald formula (MFF): LDL-C (mg/dl) = Non-HDL-C x 90% - TG x 10%.
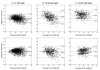
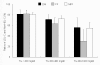
Results: Linear regression showed a significant correlation (P < 0.001) between the measured and calculated LDL-C values. Bland-Altman plots indicated that the methods (DM/MFF) were in better agreement than those (DM/FF). The LDL-C/Non-HDL-C ratio in FF calculated values was significantly lower (P < 0.05) than that in MFF or DM values, while no significant difference between MFF and DM was found. In Group A and Group B, 4.26% and 14.79% of the MFF calculated values had more than 20% deviation from those measured by DM. These percentages were significantly lower than those calculated by FF, where 7.30% and 25.63% were observed, respectively (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001). The MFF calculated values were all positive even in Group C.
Conclusions: Compared with the FF calculation, serum LDL-C values estimated by our modified formula are closer to those measured by a direct assay. The modification significantly diminishes the interference caused by hypertriglyceridemia.
Figures

References
-
- Cheng AY, Leiter LA. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006;21:400–4. - PubMed
-
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–421. - PubMed
-
- Keevil JG, Cullen MW, Gangnon R, McBride PE, Stein JH. Implications of cardiac risk and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol distributions in the United States for the diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia: data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999 to 2002. Circulation. 2007;115:1363–70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.645473. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18:499–502. - PubMed
-
- McNamara JR, Cohn JS, Wilson PW, Schaefer EJ. Calculated values for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the assessment of lipid abnormalities and coronary disease risk. Clin Chem. 1990;36:36–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

