Lymphatic biodistribution of polylactide nanoparticles
- PMID: 20487681
- PMCID: PMC3699327
Lymphatic biodistribution of polylactide nanoparticles
Erratum in
- Mol Imaging. 2011 Feb;10(1):78
Abstract
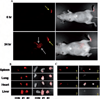
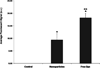
Tumor metastases occur through both the cardiovascular and lymphatic circulations. However, the majority of nanoparticle biodistribution studies have been focused on the cardiovascular circulation. In this study, we report the formulation of Cy5-labeled polylactide (Cy5-PLA) nanoparticles with controlled size and surface features and the subsequent evaluation of their lymphatic biodistribution. Cy5-PLA nanoparticles were formulated through Cy5/(BDI)ZnN(TMS)2-mediated [(BDI) = 2-((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)amido)-4-((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-imino)-2-pentene] ring-opening polymerization of lactide followed by nanoprecipitation. Their lymphatic biodistribution was evaluated by using whole-body fluorescence imaging of nude mice and ex vivo fluorescence imaging of the resected organs. This technique has the potential for providing optical contrast and drug delivery through the lymphatic circulation for the treatment of metastatic cancer.
Figures

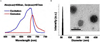

Similar articles
-
Polylactide nanoparticles containing stably incorporated cyanine dyes for in vitro and in vivo imaging applications.Microsc Res Tech. 2010 Sep;73(9):901-9. doi: 10.1002/jemt.20824. Microsc Res Tech. 2010. PMID: 20146347
-
Ring-opening polymerization-mediated controlled formulation of polylactide-drug nanoparticles.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Apr 8;131(13):4744-54. doi: 10.1021/ja8084675. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19281160
-
The formulation of aptamer-coated paclitaxel-polylactide nanoconjugates and their targeting to cancer cells.Biomaterials. 2010 Apr;31(11):3043-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20122727 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in lymphatic imaging and drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011 Sep 10;63(10-11):876-85. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2011.05.020. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011. PMID: 21718728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soft- and hard-lipid nanoparticles: a novel approach to lymphatic drug delivery.Arch Pharm Res. 2018 Aug;41(8):797-814. doi: 10.1007/s12272-018-1060-0. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Arch Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30074202 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-functionalized, ultra-small, monodisperse silica nanoconjugates for targeted dual-modal imaging of lymph nodes with metastatic tumors.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012 Dec 14;51(51):12721-6. doi: 10.1002/anie.201205271. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012. PMID: 23136130 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Highly Sensitive Detection of Bacteria by Binder-Coupled Multifunctional Polymeric Dyes.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jun 18;15(12):2723. doi: 10.3390/polym15122723. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37376368 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Conjugated Toll-Like Receptor 9 Agonists Improve the Potency, Durability, and Breadth of COVID-19 Vaccines.ACS Nano. 2024 Jan 30;18(4):3214-3233. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c09700. Epub 2024 Jan 12. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38215338 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent Polymer Nanoparticles Based on Dyes: Seeking Brighter Tools for Bioimaging.Small. 2016 Apr;12(15):1968-92. doi: 10.1002/smll.201503396. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Small. 2016. PMID: 26901678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical Size Limit of Biodegradable Nanoparticles for Enhanced Lymph Node Trafficking and Paracortex Penetration.Nano Res. 2019 Apr;12(4):837-844. doi: 10.1007/s12274-019-2301-3. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Nano Res. 2019. PMID: 33343832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Witte MH, Way DL, Witte CL, Bernas M. Lymphagiogenesis: mechanisms, significance and clinical implications. EXS. 1997;79:65–112. - PubMed
-
- Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991;64:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Weiss L, Schmidschonbein GW. Biomechanical interactions of cancer cells with the microvasculature during metastasis. Cell Biophys. 1989;14:187–215. - PubMed
-
- Pepper MS, Tille JC, Nisato R, Skobe M. Lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;314:167–177. - PubMed
-
- de Boer M, van Deurzen CHM, van Dijck J, et al. Micrometastases or isolated tumor cells and the outcome of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;13:653–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
