O-GlcNAc cycling: emerging roles in development and epigenetics
- PMID: 20488252
- PMCID: PMC2917487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.05.001
O-GlcNAc cycling: emerging roles in development and epigenetics
Abstract
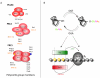
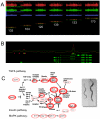
The nutrient-sensing hexosamine signaling pathway modulates the levels of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) on key targets impacting cellular signaling, protein turnover and gene expression. O-GlcNAc cycling may be deregulated in neurodegenerative disease, cancer, and diabetes. Studies in model organisms demonstrate that the O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT/Sxc) is essential for Polycomb group (PcG) repression of the homeotic genes, clusters of genes responsible for the adult body plan. Surprisingly, from flies to man, the O-GlcNAcase (OGA, MGEA5) gene is embedded within the NK cluster, the most evolutionarily ancient of three homeobox gene clusters regulated by PcG repression. PcG repression also plays a key role in maintaining stem cell identity, recruiting the DNA methyltransferase machinery for imprinting, and in X-chromosome inactivation. Intriguingly, the Ogt gene resides near the Xist locus in vertebrates and is subject to regulation by PcG-dependent X-inactivation. OGT is also an enzymatic component of the human dosage compensation complex. These 'evo-devo' relationships linking O-GlcNAc cycling to higher order chromatin structure provide insights into how nutrient availability may influence the epigenetic regulation of gene expression. O-GlcNAc cycling at promoters and PcG repression represent concrete mechanisms by which nutritional information may be transmitted across generations in the intra-uterine environment. Thus, the nutrient-sensing hexosamine signaling pathway may be a key contributor to the metabolic deregulation resulting from prenatal exposure to famine, or the 'vicious cycle' observed in children of mothers with type-2 diabetes and metabolic disease.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Love D, Hanover J. The hexosamine signaling pathway: deciphering the “O-GlcNAc code”. Sci STKE. 2005;2005:re13. - PubMed
-
- Kelly W, Hart G. Glycosylation of chromosomal proteins: localization of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine in Drosophila chromatin. Cell. 1989;57:243–251. - PubMed
-
- Kelly W, Dahmus M, Hart G. RNA polymerase II is a glycoprotein. Modification of the COOH-terminal domain by O-GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:10416–10424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

