Alpha4beta7 integrin/MAdCAM-1 adhesion pathway is crucial for B cell migration into pancreatic lymph nodes in nonobese diabetic mice
- PMID: 20488663
- PMCID: PMC2926266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2010.04.002
Alpha4beta7 integrin/MAdCAM-1 adhesion pathway is crucial for B cell migration into pancreatic lymph nodes in nonobese diabetic mice
Abstract
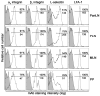
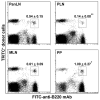
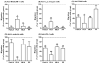
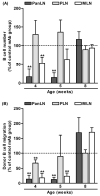
Although B cells are crucial antigen-presenting cells in the initiation of T cell autoimmunity to islet beta cell autoantigens in type 1 diabetes (T1D), adhesion molecules that control migration of B cells into pancreatic lymph nodes (PanLN) in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse model of human T1D have not been defined. In this study, we found that B cells from PanLN of 3-4-week-old female NOD mice expressed high levels of alpha(4) integrin and LFA-1 and intermediate levels of beta(7) integrin; half of B cells were L-selectin(high). In short-term in vivo lymphocyte migration assays, B cells migrated from the bloodstream into PanLN more efficiently than into peripheral LNs. Moreover, antibodies to mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (MAdCAM-1) and alpha(4)beta(7) integrin inhibited >90% of B cell migration into PanLN. In contrast, antibodies to peripheral node addressin, L-selectin or LFA-1 partially inhibited B cell migration into PanLN. Furthermore, one intraperitoneal injection of anti-MAdCAM-1 antibody into 3-week-old NOD mice significantly inhibited entry of B cells into PanLN for at least 2 weeks. Taken together, these results indicate that the alpha(4)beta(7) integrin/MAdCAM-1 adhesion pathway plays a predominant role in migration of B cells into PanLN in NOD mice. Thus, specific blockage of alpha(4)beta(7) integrin/MAdCAM-1 adhesion pathway-mediated B cell migration may be a potential treatment for T1D.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mucosal Addressin Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Mediates T Cell Migration into Pancreas-Draining Lymph Nodes for Initiation of the Autoimmune Response in Type 1 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 22;25(21):11350. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111350. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518902 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of beta 7 integrin and mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) in the development of diabetes in obese diabetic mice.Diabetes. 1997 Oct;46(10):1542-7. doi: 10.2337/diacare.46.10.1542. Diabetes. 1997. PMID: 9313747
-
Lymphocytes infiltrating the CNS during inflammation display a distinctive phenotype and bind to VCAM-1 but not to MAdCAM-1.Int Immunol. 1995 Mar;7(3):481-91. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.3.481. Int Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7540864
-
The role of alpha 4 integrins in lung pathophysiology.Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996 Aug;22:104s-108s. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8871053 Review.
-
The roles of alpha 4-integrins in the development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998;231:65-83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71987-5_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9479861 Review.
Cited by
-
CCR2 inhibition sequesters multiple subsets of leukocytes in the bone marrow.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 24;5:11664. doi: 10.1038/srep11664. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26206182 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary gluten alters the balance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in T cells of BALB/c mice.Immunology. 2013 Jan;138(1):23-33. doi: 10.1111/imm.12007. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 22913724 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal Addressin Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Mediates T Cell Migration into Pancreas-Draining Lymph Nodes for Initiation of the Autoimmune Response in Type 1 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 22;25(21):11350. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111350. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518902 Free PMC article.
-
Vedolizumab Tissue Concentration Correlates to Mucosal Inflammation and Objective Treatment Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021 Oct 20;27(11):1813-1820. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izab053. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021. PMID: 33705545 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating complex peptide structures using macrocycle conformational maps.RSC Chem Biol. 2022 Apr 19;3(6):739-747. doi: 10.1039/d2cb00016d. eCollection 2022 Jun 8. RSC Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35755184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson MS, Bluestone JA. The NOD mouse: a model of immune dysregulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:447–85. - PubMed
-
- Serreze DV, Chapman HD, Varnum DS, Hanson MS, Reifsnyder PC, Richard SD, Fleming SA, Leiter EH, Shultz LD. B lymphocytes are essential for the initiation of T cell-mediated autoimmune diabetes: analysis of a new “speed congenic” stock of NOD.Ig mu null mice. J Exp Med. 1996;184:2049–53. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Silveira PA, Grey ST. B cells in the spotlight: innocent bystanders or major players in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17:128–35. - PubMed
-
- Yang M, Charlton B, Gautam AM. Development of insulitis and diabetes in B cell-deficient NOD mice. J Autoimmun. 1997;10:257–60. - PubMed
-
- Noorchashm H, Noorchashm N, Kern J, Rostami SY, Barker CF, Naji A. B-cells are required for the initiation of insulitis and sialitis in nonobese diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1997;46:941–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

