Efficacy and safety of different doses and retreatment of rituximab: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial in patients who are biological naive with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate (Study Evaluating Rituximab's Efficacy in MTX iNadequate rEsponders (SERENE))
- PMID: 20488885
- PMCID: PMC2938895
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.119933
Efficacy and safety of different doses and retreatment of rituximab: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial in patients who are biological naive with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate (Study Evaluating Rituximab's Efficacy in MTX iNadequate rEsponders (SERENE))
Erratum in
- Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Aug;70(8):1519
Abstract
Objectives: This phase III study evaluated the efficacy and safety of rituximab plus methotrexate (MTX) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had an inadequate response to MTX and who were naïve to prior biological treatment.
Methods: Patients with active disease on stable MTX (10-25 mg/week) were randomised to rituximab 2 x 500 mg (n=168), rituximab 2 x 1000 mg (n=172), or placebo (n=172). From week 24, patients not in remission (Disease Activity Score (28 joints) > or =2.6) received a second course of rituximab; patients initially assigned to placebo switched to rituximab 2 x 500 mg. The primary end point was American College of Rheumatology 20 (ACR20) response at week 24. All patients were followed until week 48.
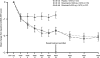
Results: At week 24, both doses of rituximab showed statistically superior efficacy (p<0.0001) to placebo (ACR20: 54%, 51% and 23%; rituximab (2 x 500 mg) + MTX, rituximab (2 x 1000 mg) + MTX and placebo + MTX, respectively). Secondary end points were also significantly improved for both rituximab groups compared with placebo. Further improvements in both rituximab arms were observed from week 24 to week 48. Rituximab + MTX was well tolerated, demonstrating comparable safety to placebo + MTX through to week 24, and between rituximab doses through to week 48.
Conclusions: Rituximab (at 2 x 500 mg and 2 x 1000 mg) plus MTX significantly improved clinical outcomes at week 24, which were further improved by week 48. No significant differences in either clinical or safety outcomes were apparent between the rituximab doses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
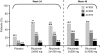
Comment in
-
Rituximab after methotrexate failure in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of the SERENE trial.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011 Nov;11(11):1515-8. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2011.608061. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21806480
References
-
- Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2572–81 - PubMed
-
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:2793–806 - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, et al. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:1390–400 - PubMed
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. Arthritis Rheum 1993;36:729–40 - PubMed
-
- Wells GA, Tugwell P, Kraag GR, et al. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient's perspective. J Rheumatol 1993;20:557–60 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

