High-throughput sequencing reveals extensive variation in human-specific L1 content in individual human genomes
- PMID: 20488934
- PMCID: PMC2928504
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.106419.110
High-throughput sequencing reveals extensive variation in human-specific L1 content in individual human genomes
Abstract
Using high-throughput sequencing, we devised a technique to determine the insertion sites of virtually all members of the human-specific L1 retrotransposon family in any human genome. Using diagnostic nucleotides, we were able to locate the approximately 800 L1Hs copies corresponding specifically to the pre-Ta, Ta-0, and Ta-1 L1Hs subfamilies, with over 90% of sequenced reads corresponding to human-specific elements. We find that any two individual genomes differ at an average of 285 sites with respect to L1 insertion presence or absence. In total, we assayed 25 individuals, 15 of which are unrelated, at 1139 sites, including 772 shared with the reference genome and 367 nonreference L1 insertions. We show that L1Hs profiles recapitulate genetic ancestry, and determine the chromosomal distribution of these elements. Using these data, we estimate that the rate of L1 retrotransposition in humans is between 1/95 and 1/270 births, and the number of dimorphic L1 elements in the human population with gene frequencies greater than 0.05 is between 3000 and 10,000.
Figures

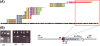
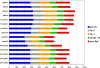
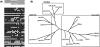
Comment in
-
Jumping genes.Nat Methods. 2010 Aug;7(8):579. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0810-579. Nat Methods. 2010. PMID: 20704015 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
