miR-192 mediates TGF-beta/Smad3-driven renal fibrosis
- PMID: 20488955
- PMCID: PMC2938591
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010020134
miR-192 mediates TGF-beta/Smad3-driven renal fibrosis
Abstract
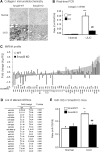
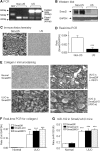
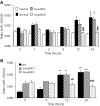
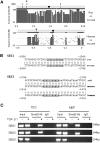
TGF-beta/Smad3 promotes renal fibrosis, but the mechanisms that regulate profibrotic genes remain unclear. We hypothesized that miR-192, a microRNA expressed in the kidney may mediate renal fibrosis in a Smad3-dependent manner. Microarray and real-time PCR demonstrated a tight association between upregulation of miR-192 in the fibrotic kidney and activation of TGF-beta/Smad signaling. Deletion of Smad7 promoted miR-192 expression and enhanced Smad signaling and fibrosis in obstructive kidney disease. In contrast, overexpression of Smad7 to block TGF-beta/Smad signaling inhibited miR-192 expression and renal fibrosis in the rat 5/6 nephrectomy model; in vitro, overexpression of Smad7 in tubular epithelial cells abolished TGF-beta1-induced miR-192 expression. Furthermore, Smad3 but not Smad2 mediated TGF-beta1-induced miR-192 expression by binding to the miR-192 promoter. Last, overexpression of a miR-192 mimic promoted and addition of a miR-192 inhibitor blocked TGF-beta1-induced collagen matrix expression. Taken together, miR-192 may be a critical downstream mediator of TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling in the development of renal fibrosis.
Figures


References
-
- Liu Y: Renal fibrosis: New insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int 69: 213–217, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bottinger EP, Bitzer M: TGF-beta signaling in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 2600–2610, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Schnaper HW, Hayashida T, Poncelet AC: It's a Smad world: Regulation of TGF-beta signaling in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 1126–1128, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Koka V, Lan HY: Transforming growth factor-beta and Smad signalling in kidney diseases. Nephrology (Carlton) 10: 48–56, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Zavadil J, Narasimhan M, Blumenberg M, Schneider RJ: Transforming growth factor-beta and microRNA:mRNA regulatory networks in epithelial plasticity. Cells Tissues Organs 185: 157–161, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

