Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in gingival overgrowth
- PMID: 20489142
- PMCID: PMC2893664
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090952
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in gingival overgrowth
Abstract
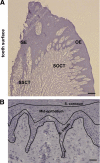
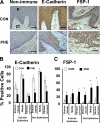
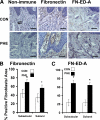
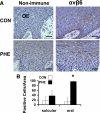
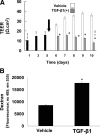
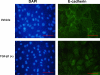
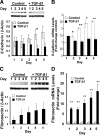
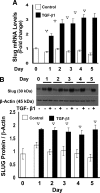
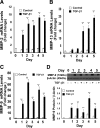
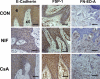
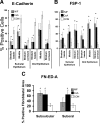
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) occurs normally in development. In pathology, EMT drives cancer and fibrosis. Medication with phenytoin, nifedipine, and cyclosporine-A often causes gingival overgrowth. Based partly on the histopathology of gingival overgrowth, the present study investigates the hypothesis that EMT could contribute to its development. We found that phenytoin-induced human gingival overgrowth tissues, the most fibrotic drug-induced variety, contain diminished epithelial E-cadherin expression, whereas fibroblast-specific protein-1 (FSP-1) and alphavbeta6 integrin levels are up-regulated. In connective tissue stroma, fibronectin and alternatively spliced fibronectin extra type III domain A (FN-ED-A) levels are increased in overgrowth lesions. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 treatment of primary human gingival epithelial cells cultured in transwell plates resulted in inhibited barrier function as determined by reduced electrical resistance, paracellular permeability assays, and cell surface E-cadherin expression. Moreover, TGF-beta1 altered the expression of other markers of EMT determined at the mRNA and protein levels: E-cadherin decreased, whereas SLUG, fibronectin, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)2, MMP9, and MMP13 increased. Nifedipine- and cyclosporine A-induced gingival overgrowth tissues similarly contain diminished E-cadherin and elevated levels of FSP-1 and fibronectin, but normal levels of alphavbeta6 integrin. In summary, data in vitro support that human gingival epithelial cells undergo functional and gene expression changes consistent with EMT in response to TGF-beta1, and in vivo studies show that important EMT markers occur in clinical gingival overgrowth tissues. These findings support the hypothesis that EMT likely occurs in drug-induced gingival overgrowth.
Figures
References
-
- Uzel MI, Kantarci A, Hong HH, Uygur C, Sheff MC, Firatli E, Trackman PC. Connective tissue growth factor in drug-induced gingival overgrowth. J Periodontol. 2001;72:921–931. - PubMed
-
- Black SA, Jr, Palamakumbura AH, Stan M, Trackman PC. Tissue-specific mechanisms for CCN2/CTGF persistence in fibrotic gingiva: interactions between cAMP and MAPK signaling pathways, and prostaglandin E2-EP3 receptor mediated activation of the c-JUN N-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:15416–15429. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black SA, Jr, Trackman PC. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGFβ1) stimulates connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) expression in human gingival fibroblasts through a RhoA-independent. Rac1/Cdc42-dependent mechanism: statins with forskolin block TGFβ1-induced CCN2/CTGF expression. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:10835–10847. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trackman PC, Kantarci A. Connective tissue metabolism and gingival overgrowth. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004;15:165–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

