Crystal structure of CCM3, a cerebral cavernous malformation protein critical for vascular integrity
- PMID: 20489202
- PMCID: PMC2911348
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.128470
Crystal structure of CCM3, a cerebral cavernous malformation protein critical for vascular integrity
Abstract
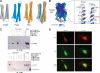
CCM3 mutations are associated with cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM), a disease affecting 0.1-0.5% of the human population. CCM3 (PDCD10, TFAR15) is thought to form a CCM complex with CCM1 and CCM2; however, the molecular basis for these interactions is not known. We have determined the 2.5 A crystal structure of CCM3. This structure shows an all alpha-helical protein containing two domains, an N-terminal dimerization domain with a fold not previously observed, and a C-terminal focal adhesion targeting (FAT)-homology domain. We show that CCM3 binds CCM2 via this FAT-homology domain and that mutation of a highly conserved FAK-like hydrophobic pocket (HP1) abrogates CCM3-CCM2 interaction. This CCM3 FAT-homology domain also interacts with paxillin LD motifs using the same surface, and partial CCM3 co-localization with paxillin in cells is lost on HP1 mutation. Disease-related CCM3 truncations affect the FAT-homology domain suggesting a role for the FAT-homology domain in the etiology of CCM.
Figures



References
-
- Labauge P., Denier C., Bergametti F., Tournier-Lasserve E. (2007) Lancet Neurol. 6, 237–244 - PubMed
-
- Sahoo T., Johnson E. W., Thomas J. W., Kuehl P. M., Jones T. L., Dokken C. G., Touchman J. W., Gallione C. J., Lee-Lin S. Q., Kosofsky B., Kurth J. H., Louis D. N., Mettler G., Morrison L., Gil-Nagel A., Rich S. S., Zabramski J. M., Boguski M. S., Green E. D., Marchuk D. A. (1999) Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 2325–2333 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

