Application of direct renin inhibition to chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 20490905
- PMCID: PMC2887501
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-010-6232-1
Application of direct renin inhibition to chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Purpose: Chronic kidney disease has serious implications with a high risk for progressive loss of renal function, increased cardiovascular events as well as a substantial financial burden. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is activated in chronic kidney disease, especially in diabetes and hypertension, which are the leading causes of chronic kidney disease. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) decrease the rate of progression of diabetic and non-diabetic nephropathy and are recommended therapy for chronic kidney disease.
Methods: Key clinical trials supporting the use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs in chronic kidney disease are discussed. Recent developments in our understanding of RAAS biology and the use of direct renin inhibition are reviewed in the context of their potential impact on the prevention and management of chronic kidney disease.
Results: Despite the clinical success of ACE inhibitors and ARBs the rates of mortality and progression to renal failure remain high in these patient populations. ACE inhibitor or ARB monotherapy, in doses commonly used in clinical practice does not result in complete suppression of the RAAS. Aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, offers a novel approach to inhibit the RAAS in chronic kidney disease.
Conclusions: High dose ARB therapy or combination therapies with ACE inhibitors and ARBs have shown beneficial effects on surrogate markers of chronic kidney disease. Early data based on urinary protein excretion rates as a surrogate marker for renal function suggest a possibly novel role for aliskiren alone or in combination with ARBs in chronic kidney disease.
Figures
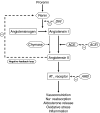
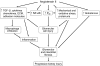

References
-
- K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 2002; 39:S1−266. - PubMed
-
- MMWR Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated risk factors—United States, 1999–2004. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56:161–165. - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System.Available at: www.usrds.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

