Zn²(+) -containing protein S inhibits extrinsic factor X-activating complex independently of tissue factor pathway inhibitor
- PMID: 20492471
- PMCID: PMC2955986
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03919.x
Zn²(+) -containing protein S inhibits extrinsic factor X-activating complex independently of tissue factor pathway inhibitor
Abstract
Background: Protein S (PS) has direct anticoagulant activity, independently of activated protein C (APC). The mechanisms underlying this activity remain unclear, because PS preparations differ in activity, giving rise to conflicting results. Some purification procedures result in loss of intramolecular Zn²(+) , which is essential for inhibition of prothrombinase.
Objective: To investigate the inhibition of extrinsic factor (F)Xase by Zn²(+) -containing PS.
Methods: Purified component extrinsic FXase assays were used to determine FXa generation in the presence and absence of PS and/or tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). Binding assays, immunoblots and thrombin generation assays in plasma supported the FXase data.
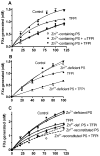
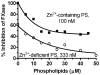
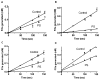
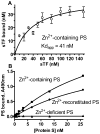
Results: Zn²(+) -containing PS potently inhibited extrinsic FXase in the presence of saturating phospholipids, independently of TFPI, whereas inhibition of extrinsic FXase by Zn²(+) -deficient PS required TFPI. Immunoblots for FXa and functional assays showed that Zn²(+) -containing PS inhibited primarily the quantity of FXa formed by tissue factor (TF)-FVIIa, rather than FXa amidolytic activity. Zn²(+) -containing PS, but not Zn²(+) -deficient PS, bound to TF with high affinity (K(dapp) = 41 nm) and targeted TF function. Binding of PS to FVIIa was negligible, whereas PS showed appreciable binding to FX. Increasing FX concentrations 10-fold reduced PS inhibition five-fold, suggesting that PS inhibition of FXase is FX-dependent. PS also exhibited TFPI-independent and APC-independent anticoagulant activity during TF-initiated thrombin generation in plasma.
Conclusions: PS that retains native Zn²(+) also retains anticoagulant functions independently of APC and TFPI. Inhibition of extrinsic FXase by PS at saturating levels of phospholipids depends on PS retention of intramolecular Zn²(+) , interaction with FX, and, particularly, interaction with TF.
© 2010 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
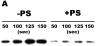
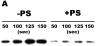



References
-
- Dahlback B. The tale of protein S and C4b-binding protein, a story of affection. Thromb Haemost. 2007;98:90–6. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz HP, Fischer M, Hopmeier P, Batard MA, Griffin JH. Plasma protein S deficiency in familial thrombotic disease. Blood. 1984;64:1297–300. - PubMed
-
- Mahasandana C, Suvatte V, Marlar RA, Manco-Johnson MJ, Jacobson LJ, Hathaway WE. Neonatal purpura fulminans associated with homozygous protein S deficiency (Letter) Lancet. 1990;335:61–2. - PubMed
-
- Walker FJ, Chavin SI, Fay PJ. Inactivation of factor VIII by activated protein C and protein S. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987;252:322–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

