The phosphoCTD-interacting domain of Topoisomerase I
- PMID: 20493173
- PMCID: PMC2900466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.081
The phosphoCTD-interacting domain of Topoisomerase I
Abstract
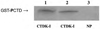
The N-terminal domain (NTD) of Drosophila melanogaster (Dm) Topoisomerase I has been shown to bind to RNA polymerase II, but the domain of RNAPII with which it interacts is not known. Using bacterially-expressed fusion proteins carrying all or half of the NTDs of Dm and human (Homo sapiens, Hs) Topo I, we demonstrate that the N-terminal half of each NTD binds directly to the hyperphosphorylated C-terminal repeat domain (phosphoCTD) of the largest RNAPII subunit, Rpb1. Thus, the amino terminal segment of metazoan Topo I (1-157 for Dm and 1-114 for Hs) contains a novel phosphoCTD-interacting domain that we designate the Topo I-Rpb1 interacting (TRI) domain. The long-known in vivo association of Topo I with active genes presumably can be attributed, wholly or in part, to the TRI domain-mediated binding of Topo I to the phosphoCTD of transcribing RNAPII.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Gilmour DS, Pflugfelder G, Wang JC, Lis JT. Topoisomerase I interacts with transcribed regions in Drosophila cells. Cell. 1986;44:401–407. - PubMed
-
- Gilmour DS, Elgin SC. Association of topoisomerase I with transcriptionally active loci in Drosophila. Nci Monogr. 1987;1987:17–21. - PubMed
-
- Carty SM, Greenleaf AL. Hyperphosphorylated C-terminal repeat domain-associating proteins in the nuclear proteome link transcription to DNA/chromatin modification and RNA processing. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2002;1:598–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

