Use of magnetically purified Plasmodium falciparum parasites improves the accuracy of erythrocyte invasion assays
- PMID: 20493844
- PMCID: PMC2940115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exppara.2010.05.007
Use of magnetically purified Plasmodium falciparum parasites improves the accuracy of erythrocyte invasion assays
Abstract
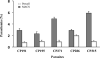
Merozoite invasion of erythrocytes is a crucial step for the asexual cycle of Plasmodium falciparum. Multiple invasion pathways, which involve different ligand-receptor interactions, have been identified in P. falciparum by examining the entry of purified parasite into erythrocytes with different surface receptors, either mutant or under different enzyme treatments. The most critical step for a successful invasion assay is the isolation of erythrocytes infected with viable schizonts. Here, we applied a magnetic column to purify the schizonts for the erythrocyte invasion assay. Comparing to Percoll-sorbitol purification method, this modified approach showed great improvement on reproducibility and reliability of invasion assay, particularly for short-term, culture-adapted parasite isolates. The magnetic purification method is an excellent alternative for parasite isolates that do not tolerate or with unknown sensitivity to Percoll-sorbitol exposure.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
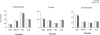
Similar articles
-
Magnetic isolation of Plasmodium falciparum schizonts iRBCs to generate a high parasitaemia and synchronized in vitro culture.Malar J. 2014 Mar 21;13:112. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-112. Malar J. 2014. PMID: 24655321 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the in vitro invasive capabilities of Plasmodium falciparum schizonts isolated by Percoll gradient or using magnetic based separation.Malar J. 2011 Apr 18;10:96. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-96. Malar J. 2011. PMID: 21501476 Free PMC article.
-
A modified two-color flow cytometry assay to quantify in-vitro reinvasion and determine invasion phenotypes at low Plasmodium falciparum parasitemia.Exp Parasitol. 2020 Nov;218:107969. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2020.107969. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Exp Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32858043
-
Cytoskeletal and membrane remodelling during malaria parasite invasion of the human erythrocyte.Br J Haematol. 2011 Sep;154(6):680-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08766.x. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Br J Haematol. 2011. PMID: 21718279 Review.
-
Invasion by P. falciparum merozoites suggests a hierarchy of molecular interactions.PLoS Pathog. 2005 Dec;1(4):e37. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0010037. Epub 2005 Dec 16. PLoS Pathog. 2005. PMID: 16362075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gellan sulfate inhibits Plasmodium falciparum growth and invasion of red blood cells in vitro.Sci Rep. 2014 Apr 17;4:4723. doi: 10.1038/srep04723. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24740150 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic isolation of Plasmodium falciparum schizonts iRBCs to generate a high parasitaemia and synchronized in vitro culture.Malar J. 2014 Mar 21;13:112. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-112. Malar J. 2014. PMID: 24655321 Free PMC article.
-
Improving malaria control in West Africa: interruption of transmission as a paradigm shift.Acta Trop. 2012 Mar;121(3):175-83. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2011.11.009. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Acta Trop. 2012. PMID: 22142790 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the in vitro invasive capabilities of Plasmodium falciparum schizonts isolated by Percoll gradient or using magnetic based separation.Malar J. 2011 Apr 18;10:96. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-96. Malar J. 2011. PMID: 21501476 Free PMC article.
-
Protocols for Plasmodium gametocyte production in vitro: an integrative review and analysis.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Dec 5;15(1):451. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05566-3. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 36471426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fairhurst RM, Baruch DI, Brittain NJ, Ostera GR, Wallach JS, Hoang HL, Hayton K, Guindo A, Makobongo MO, Schwartz OM, Tounkara A, Doumbo OK, Diallo DA, Fujioka H, Ho M, Wellems TE. Abnormal display of PfEMP-1 on erythrocytes carrying haemoglobin C may protect against malaria. Nature. 2005;435:1117–1121. - PubMed
-
- Gaur D, Mayer DC, Miller LH. Parasite ligand-host receptor interactions during invasion of erythrocytes by Plasmodium merozoites. International Journal for Parasitology. 2004;34:1413–1429. - PubMed
-
- Ginsburg H, Landau I, Baccam D, Mazier D. Fractionation of mouse malarious blood according to parasite developmental stage, using a Percoll-sorbitol gradient. Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée. 1987;62:418–425. - PubMed
-
- Goodyer ID, Johnson J, Eisenthal R, Hayes DJ. Purification of mature-stage Plasmodium falciparum by gelatine flotation. Annals Tropical Medicine Parasitology. 1994;88:209–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

