The LysR-type transcriptional regulator QseD alters type three secretion in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and motility in K-12 Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20494990
- PMCID: PMC2897335
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00382-10
The LysR-type transcriptional regulator QseD alters type three secretion in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and motility in K-12 Escherichia coli
Abstract
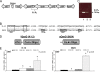
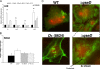
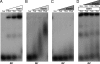
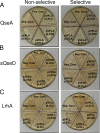
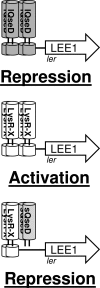
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 responds to the host-produced epinephrine and norepinephrine, and bacterially produced autoinducer 3 (AI-3), through two-component systems. Further integration of multiple regulatory signaling networks, involving regulators such as the LysR-type transcriptional regulator (LTTR) QseA, promotes effective regulation of virulence factors. These include the production of flagella, a phage-encoded Shiga toxin, and genes within the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) responsible for attaching and effacing (AE) lesion formation. Here, we describe a new member of this signaling cascade, an LTTR heretofore renamed QseD (quorum-sensing E. coli regulator D). QseD is present in all enterobacteria but exists almost exclusively in O157:H7 isolates as a helix-turn-helix (HTH) truncated isoform. This "short" isoform (sQseD) is still able to regulate gene expression through a different mechanism than the full-length K-12 E. coli "long" QseD isoform (lQseD). The EHEC Delta qseD mutant exhibits increased expression of all LEE operons and deregulation of AE lesion formation. The loss of qseD in EHEC does not affect motility, but the K-12 Delta qseD mutant is hypermotile. While the lQseD directly binds to the ler promoter, encoding the LEE master regulator, to repress LEE transcription, the sQseD isoform does not. LTTRs bind to DNA as tetramers, and these data suggest that sQseD regulates ler by forming heterotetramers with another LTTR. The LTTRs known to regulate LEE transcription, QseA and LrhA, do not interact with sQseD, suggesting that sQseD acts as a dominant-negative partner with a yet-unidentified LTTR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quorum-sensing Escherichia coli regulator A: a regulator of the LysR family involved in the regulation of the locus of enterocyte effacement pathogenicity island in enterohemorrhagic E. coli.Infect Immun. 2002 Jun;70(6):3085-93. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.6.3085-3093.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12011002 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinate control of the locus of enterocyte effacement and enterohemolysin genes by multiple common virulence regulators in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2011 Nov;79(11):4628-37. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05023-11. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21844237 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence meets metabolism: Cra and KdpE gene regulation in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.mBio. 2012 Oct 16;3(5):e00280-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00280-12. mBio. 2012. PMID: 23073764 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing and expression of virulence in Escherichia coli O157:H7.Int J Food Microbiol. 2003 Aug 15;85(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(02)00482-8. Int J Food Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12810266 Review.
-
The Epinephrine/Norepinephrine/Autoinducer-3 Interkingdom Signaling System in Escherichia coli O157:H7.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;874:247-61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-20215-0_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26589223 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Tetrameric Assembly Configuration in VV2_1132, a LysR-Type Transcriptional Regulator in Vibrio vulnificus.Mol Cells. 2018 Apr 30;41(4):301-310. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.2190. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Mol Cells. 2018. PMID: 29487273 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a hypochlorite-specific transcription factor from Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6892-903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.287219. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22223481 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of a LysR Transcriptional Regulator to Listeria monocytogenes Virulence and Identification of Its Regulons.J Bacteriol. 2020 Apr 27;202(10):e00087-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00087-20. Print 2020 Apr 27. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32179628 Free PMC article.
-
Novel function of single-target regulator NorR involved in swarming motility and biofilm formation revealed in Vibrio alginolyticus.BMC Biol. 2024 Nov 6;22(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02057-y. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39506750 Free PMC article.
-
LysR-type transcriptional regulator OvrB encoded in O island 9 drives enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 virulence.Virulence. 2019 Dec;10(1):783-792. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1661721. Virulence. 2019. PMID: 31502495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, K. J., D. Lepp, R. C. McKellar, and M. W. Griffiths. 2008. Examination of stress and virulence gene expression in Escherichia coli O157:H7 using targeted microarray analysis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 5:437-447. - PubMed
-
- Alto, N. M., A. W. Weflen, M. J. Rardin, D. Yarar, C. S. Lazar, R. Tonikian, A. Koller, S. S. Taylor, C. Boone, S. S. Sidhu, S. L. Schmid, G. A. Hecht, and J. E. Dixon. 2007. The type III effector EspF coordinates membrane trafficking by the spatiotemporal activation of two eukaryotic signaling pathways. J. Cell Biol. 178:1265-1278. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amberg, D. C., D. Burke, J. N. Strathern, and Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. 2005. Methods in yeast genetics: a Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory course manual, 2005 ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

