Structure-activity analysis of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal molecule
- PMID: 20494992
- PMCID: PMC2897350
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00081-10
Structure-activity analysis of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal molecule
Abstract
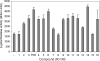
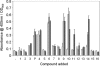
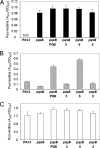
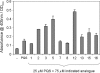
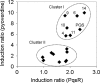
We synthesized a range of PQS (Pseudomonas quinolone signal; 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone) analogues and tested them for their ability to stimulate MvfR-dependent pqsA transcription, MvfR-independent pyoverdine production, and membrane vesicle production. The structure-activity profile of the PQS analogues was different for each of these phenotypes. Certain inactive PQS analogues were also found to strongly synergize PQS-dependent pyoverdine production.
Figures


References
-
- Bredenbruch, F., R. Geffers, M. Nimtz, J. Buer, and S. Häussler. 2006. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal (PQS) has an iron-chelating activity. Environ. Microbiol. 8:1318-1329. - PubMed
-
- Collier, D. N., L. Anderson, S. L. McKnight, T. L. Noah, M. Knowles, R. Boucher, U. Schwab, P. Gilligan, and E. C. Pesci. 2002. A bacterial cell to cell signal in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 215:41-46. - PubMed
-
- Cugini, C., M. W. Calfee, J. M. Farrow, D. K. Morales, E. C. Pesci, and D. A. Hogan. 2007. Farnesol, a common sesquiterpene, inhibits PQS production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 65:896-906. - PubMed
-
- Deziel, E., S. Gopalan, A. P. Tampakaki, F. Lepine, K. E. Padfield, M. Saucier, G. Xiao, and L. G. Rahme. 2005. The contribution of MvfR to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis and quorum sensing circuitry regulation: multiple quorum sensing-regulated genes are modulated without affecting lasRI, rhlRI or the production of N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones. Mol. Microbiol. 55:998-1014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

