Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity is associated with miR-146a-induced inhibition of the neuregulin-ErbB pathway
- PMID: 20495188
- PMCID: PMC2920811
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvq148
Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity is associated with miR-146a-induced inhibition of the neuregulin-ErbB pathway
Abstract
Aims: A significant increase in congestive heart failure (CHF) was reported when the anti-ErbB2 antibody trastuzumab was used in combination with the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin (Dox). The aim of the present study was to investigate the role(s) of miRNAs in acute Dox-induced cardiotoxicity.
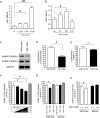
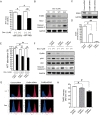
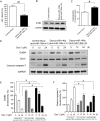
Methods and results: Neuregulin-1-ErbB signalling is essential for maintaining adult cardiac function. We found a significant reduction in ErbB4 expression in the hearts of mice after Dox treatment. Because the proteasome pathway was only partially involved in the reduction of ErbB4 expression, we examined the involvement of microRNAs (miRs) in the reduction of ErbB4 expression. miR-146a was shown to be up-regulated by Dox in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Using a luciferase reporter assay and overexpression of miR-146a, we confirmed that miR-146a targets the ErbB4 3'UTR. After Dox treatment, overexpression of miR-146a, as well as that of siRNA against ErbB4, induced cell death in cardiomyocytes. Re-expression of ErbB4 in miR-146a-overexpressing cardiomyocytes ameliorated Dox-induced cell death. To examine the loss of miR-146a function, we constructed 'decoy' genes that had tandem complementary sequences for miR-146a in the 3'UTR of a luciferase gene. When miR-146a 'decoy' genes were introduced into cardiomyocytes, ErbB4 expression was up-regulated and Dox-induced cell death was reduced.
Conclusion: These findings suggested that the up-regulation of miR-146a after Dox treatment is involved in acute Dox-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting ErbB4. Inhibition of both ErbB2 and ErbB4 signalling may be one of the reasons why those patients who receive concurrent therapy with Dox and trastuzumab suffer from CHF.
Figures


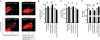
Similar articles
-
Intravenous administration of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes protects against doxorubicin/trastuzumab-induced cardiac toxicity.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Feb 1;116(2):383-392. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz108. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31098627
-
miR-146a attenuates apoptosis and modulates autophagy by targeting TAF9b/P53 pathway in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Sep 11;10(9):668. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1901-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31511497 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydroevodiamine Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Regulating Neuregulin-1/ErbB Signaling.Cardiovasc Ther. 2024 Dec 7;2024:5538740. doi: 10.1155/cdr/5538740. eCollection 2024. Cardiovasc Ther. 2024. PMID: 39742014 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotoxicity in signal transduction therapeutics: erbB2 antibodies and the heart.Semin Oncol. 2001 Oct;28(5 Suppl 16):18-26. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90278-7. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11706392 Review.
-
Neuregulin-1 signalling and antipsychotic treatment: potential therapeutic targets in a schizophrenia candidate signalling pathway.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Mar;226(2):201-15. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3003-2. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23389757 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuregulin-1 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt and inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Nov;370(1-2):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1395-7. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22886427
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiomyocyte Death in Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 3;8:434. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00434. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32582710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early assessment of acute coronary syndromes in the emergency department: the potential diagnostic value of circulating microRNAs.EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Nov;4(11):1176-85. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201749. Epub 2012 Oct 1. EMBO Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 23023917 Free PMC article.
-
Oridonin exerts anticancer effect on osteosarcoma by activating PPAR-γ and inhibiting Nrf2 pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 11;9(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0031-6. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29323103 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling in the hippocampus of rats after administration of doxorubicin.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Jan 30;12:231-239. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S151511. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29430172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li JY, Wang H, May S, Song X, Fueyo J, Fuller GN. Constitutive activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase correlates with histologic grade and EGFR expression in diffuse gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2008;88:11–17. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9529-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Spector NL, Blackwell KL. Understanding the mechanisms behind trastuzumab therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5838–5847. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.22.1507. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao YY, Sawyer DR, Baliga RR, Opel DJ, Han X, Marchionni MA, et al. Neuregulins promote survival and growth of cardiac myocytes. Persistence of ErbB2 and ErbB4 expression in neonatal and adult ventricular myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:10261–10269. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.17.10261. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:127–137. doi:10.1038/35052073. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

