Genetic variation in microRNA networks: the implications for cancer research
- PMID: 20495573
- PMCID: PMC2950312
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc2867
Genetic variation in microRNA networks: the implications for cancer research
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Jul;10(7):523
Abstract
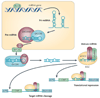
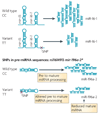
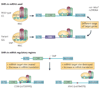
Many studies have highlighted the role that microRNAs have in physiological processes and how their deregulation can lead to cancer. More recently, it has been proposed that the presence of single nucleotide polymorphisms in microRNA genes, their processing machinery and target binding sites affects cancer risk, treatment efficacy and patient prognosis. In reviewing this new field of cancer biology, we describe the methodological approaches of these studies and make recommendations for which strategies will be most informative in the future.
Figures

References
-
-
Frazer KA, et al. A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature. 2007;449:851–861.This paper provides a good background to HapMap and provides details of the most recent version of the database.
-
-
-
Kan YW, Dozy AM. Polymorphism of DNA sequence adjacent to human beta-globin structural gene: relationship to sickle mutation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1978;75:5631–5635.A seminal study that describes the first detection of SNPs
-
-
-
Bartel B. MicroRNAs directing siRNA biogenesis. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005;12:569–571.This is an excellent paper that covers miRNA biogenesis in a complete and descriptive manner.
-
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

