Post-transcriptional control during chronic inflammation and cancer: a focus on AU-rich elements
- PMID: 20495997
- PMCID: PMC2921490
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0383-x
Post-transcriptional control during chronic inflammation and cancer: a focus on AU-rich elements
Abstract
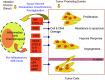
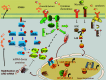
A considerable number of genes that code for AU-rich mRNAs including cytokines, growth factors, transcriptional factors, and certain receptors are involved in both chronic inflammation and cancer. Overexpression of these genes is affected by aberrations or by prolonged activation of several signaling pathways. AU-rich elements (ARE) are important cis-acting short sequences in the 3'UTR that mediate recognition of an array of RNA-binding proteins and affect mRNA stability and translation. This review addresses the cellular and molecular mechanisms that are common between inflammation and cancer and that also govern ARE-mediated post-transcriptional control. The first part examines the role of the ARE-genes in inflammation and cancer and sequence characteristics of AU-rich elements. The second part addresses the common signaling pathways in inflammation and cancer that regulate the ARE-mediated pathways and how their deregulations affect ARE-gene regulation and disease outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Blackshear PJ. Tristetraprolin and other CCCH tandem zinc-finger proteins in the regulation of mRNA turnover. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30:945–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

