Diagnostic imaging in COPD
- PMID: 20496297
- PMCID: PMC4334134
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1254068
Diagnostic imaging in COPD
Abstract
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a pathological pulmonary condition characterized by expiratory airflow obstruction due to emphysematous destruction of the lung parenchyma and small airways remodeling. Although spirometry is a very useful diagnostic tool for screening large groups of smokers, it cannot readily differentiate the etiologies of COPD and thus has limited utility in characterizing subjects for clinical and investigational purposes. There has been a longstanding interest in thoracic imaging and its role in the in vivo characterization of smoking-related lung disease. Research in this area has spanned readily available modalities such as chest -ray and computed tomography to more advanced imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Although the chest x-ray is almost universally available, it lacks sensitivity in detecting both airway disease and mild emphysema and is not generally amenable to objective analysis. Computed tomography has become the standard modality to objectively visualize lung disease. It can provide useful measures of the presence and extent of emphysema, airway disease, and, more recently, pulmonary vascular disease for clinical correlation. It does, however, face limitations in standardization across brands and generations of scanners, and the ionizing radiation associated with image acquisition is of concern to both patients and health care providers. Newer techniques such as OCT and MRI offer exciting in vivo insights into lung structure and function that were previously available only in necropsy specimens and physiology laboratories. Given the more limited availability of these techniques, they will be viewed here as adjuncts to computed tomographic imaging.
Figures

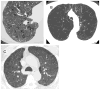
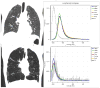

References
-
- Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Ma P, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and World Health Organization Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD): executive summary. Respir Care. 2001;46(8):798–825. - PubMed
-
- Fishman A, Martinez F, Naunheim K, Piantadosi S, Wise R, Ries A, Weinmann G, Wood DE. A randomized trial comparing lung-volume-reduction surgery with medical therapy for severe emphysema. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(21):2059–73. - PubMed
-
- Sutinen S, Christoforidis AJ, Klugh GA, Pratt PC. Roentgenologic Criteria for the Recognition of Nonsymptomatic Pulmonary Emphysema. Correlation between Roentgenologic Findings and Pulmonary Pathology. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965;91:69–76. - PubMed
-
- Nicklaus TM, Stowell DW, Christiansen WR, Renzetti AD., Jr The accuracy of the roentgenologic diagnosis of chronic pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966;93(6):889–99. - PubMed

