Efficient inhibition of lung cancer in murine model by plasmid-encoding VEGF short hairpin RNA in combination with low-dose DDP
- PMID: 20497582
- PMCID: PMC2890548
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-56
Efficient inhibition of lung cancer in murine model by plasmid-encoding VEGF short hairpin RNA in combination with low-dose DDP
Abstract
Background: VEGF is a well-validated target for antiangiogenic intervention in cancer. To date, RNAi technology has been proven to be a promising approach for targeted therapy. DDP is frequently used as a first-line drug in chemotherapy for lung cancer but usually causes severe toxicity. In this study, we investigated a novel strategy of administering and combining RNAi mediated VEGF-targeted therapy with DDP for treatment of lung cancer, with the aim of increasing efficacy and decreasing toxicity.
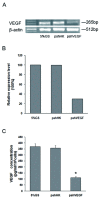
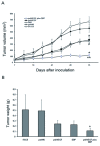
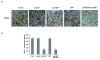
Methods: In this study, a plasmid encoding VEGF shRNA was constructed to knockdown VEGF both in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, specificity and potency of the targeting sequence were validated in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells by RT-PCR and ELISA assays. In vivo, therapy experiments were conducted on nude mice bearing A549 xenograft tumors. The VEGF shRNA expressing plasmids were administered systemically in combination with low-dose DDP on a frequent basis. The tumor volume and weight were measured. MVD, the number of apoptotic cells and proliferation index in tumor tissues were assessed by CD31, TUNEL and PCNA immunostaining.
Results: The VEGF shRNA was highly effective in attenuating VEGF expression both in vitro and in vivo. The treatment with the VEGF shRNA alone reduced the mean tumor weight by 49.40% compared with the blank control (P < 0.05). The treatment with the VEGF shRNA plus DDP yielded maximal benefits by reducing the mean tumor weight by 83.13% compared with the blank control (P < 0.01). The enhanced antitumor efficacy was associated with decreased angiogenesis and increased induction of apoptosis.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated synergistic antitumor activity of combined VEGF shRNA expressing plasmids and low-dose DDP with no overt toxicity, suggesting potential applications of the combined approach in the treatment of lung cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficient inhibition of non-small-cell lung cancer xenograft by systemic delivery of plasmid-encoding short-hairpin RNA targeting VEGF.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2010 Feb;25(1):65-73. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2009.0692. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2010. PMID: 20187798
-
Enhancement of cisplatin sensitivity in lung cancer xenografts by liposome-mediated delivery of the plasmid expressing small hairpin RNA targeting Survivin.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2012 Aug;8(4):633-41. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2012.1419. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22852473
-
[Effects of shRNA on Cisplatin-resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cell A549 via Silencing CCAT2].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 May;51(3):312-319. doi: 10.12182/20200560601. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32543135 Chinese.
-
RNAi-mediated gene silencing of vascular endothelial growth factor-C inhibits tumor lymphangiogenesis and growth of gastric cancer in vivo in mice.Tumour Biol. 2013 Jun;34(3):1493-501. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0674-6. Epub 2013 Mar 10. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23475632
-
A study of the suppressive effect on human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and angiogenesis by stable plasmid-based siRNA silencing of c-Src gene expression.Oncol Rep. 2012 Mar;27(3):628-36. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1602. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22200682
Cited by
-
Exogenous norepinephrine attenuates the efficacy of sunitinib in a mouse cancer model.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Feb 20;33(1):21. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-21. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24555849 Free PMC article.
-
99mTc-3PRGD2 SPECT Predicts the Outcome of Endostar and Cisplatin Therapy in Xenograft Animals.Dose Response. 2019 Oct 20;17(4):1559325819882544. doi: 10.1177/1559325819882544. eCollection 2019 Oct-Dec. Dose Response. 2019. PMID: 31673250 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphisms and lung cancer risk.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):6406-11. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131266 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Stromal Components on Lung Cancer Carcinogenesis.J Carcinog Mutagen. 2013 Jun 25;13(8):10.4172/2157-2518.S13-008. doi: 10.4172/2157-2518.S13-008. J Carcinog Mutagen. 2013. PMID: 24205446 Free PMC article.
-
Knocking down cyclin D1b inhibits breast cancer cell growth and suppresses tumor development in a breast cancer model.Cancer Sci. 2011 Aug;102(8):1537-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01969.x. Epub 2011 May 31. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21521417 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

