Membrane domain structures of three classes of histidine kinase receptors by cell-free expression and rapid NMR analysis
- PMID: 20498088
- PMCID: PMC2890740
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1001656107
Membrane domain structures of three classes of histidine kinase receptors by cell-free expression and rapid NMR analysis
Abstract
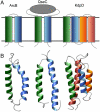
NMR structural studies of membrane proteins (MP) are hampered by complications in MP expression, technical difficulties associated with the slow process of NMR spectral peak assignment, and limited distance information obtainable for transmembrane (TM) helices. To overcome the inherent challenges in the determination of MP structures, we have developed a rapid and cost-efficient strategy that combines cell-free (CF) protein synthesis, optimized combinatorial dual-isotope labeling for nearly instant resonance assignment, and fast acquisition of long-distance information using paramagnetic probes. Here we report three backbone structures for the TM domains of the three classes of Escherichia coli histidine kinase receptors (HKRs). The ArcB and QseC TM domains are both two-helical motifs, whereas the KdpD TM domain comprises a four-helical bundle with shorter second and third helices. The interhelical distances (up to 12 A) reveal weak interactions within the TM domains of all three receptors. Determined consecutively within 8 months, these structures offer insight into the abundant and underrepresented in the Protein Data Bank class of 2-4 TM crossers and demonstrate the efficiency of our CF combinatorial dual-labeling strategy, which can be applied to solve MP structures in high numbers and at a high speed. Our results greatly expand the current knowledge of HKR structure, opening the doors to studies on their widespread and pharmaceutically important bacterial signaling mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

 ,
,  chemical shifts for valine (Val) and alanine (Ala), respectively; arrows show regions of chemical shifts corresponding to the α-helical conformation. (B and C) [1H-15N]-TROSY-HSQC spectra of 15N-labeled ArcB(1-115) expressed (B) by p-CF synthesis and in (C) E coli. (B) The precipitated protein was washed and solubilized in 5% LMPG. (C) The protein was extracted and purified from cell membrane with the FC-12 detergent and the detergent was exchanged to LMPG. Cross-peaks denoted by red arrows correspond to the tag linker residues in the E. coli-expressed protein.
chemical shifts for valine (Val) and alanine (Ala), respectively; arrows show regions of chemical shifts corresponding to the α-helical conformation. (B and C) [1H-15N]-TROSY-HSQC spectra of 15N-labeled ArcB(1-115) expressed (B) by p-CF synthesis and in (C) E coli. (B) The precipitated protein was washed and solubilized in 5% LMPG. (C) The protein was extracted and purified from cell membrane with the FC-12 detergent and the detergent was exchanged to LMPG. Cross-peaks denoted by red arrows correspond to the tag linker residues in the E. coli-expressed protein.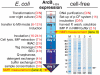
 ,
,  , and
, and  resonances.
resonances.
References
-
- Etzkorn M, et al. Plasticity of the PAS domain and a potential role for signal transduction in the histidine kinase DcuS. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15:1031–1039. - PubMed
-
- Rogov VV, et al. A new structural domain in the Escherichia coli RcsC hybrid sensor kinase connects histidine kinase and phosphoreceiver domains. J Mol Biol. 2006;364:68–79. - PubMed
-
- Marina A, Mott C, Auyzenberg A, Hendrickson WA, Waldburger CD. Structural and mutational analysis of the PhoQ histidine kinase catalytic domain. Insight into the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41182–41190. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T, et al. NMR structure of the histidine kinase domain of the E. coli osmosensor EnvZ. Nature. 1998;396:88–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

