The association of alanine transaminase with aging, frailty, and mortality
- PMID: 20498223
- PMCID: PMC4085878
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glq082
The association of alanine transaminase with aging, frailty, and mortality
Abstract
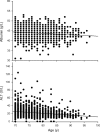
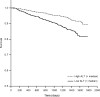
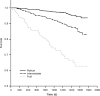
The relationships between blood tests of liver function and injury (alanine transaminase [ALT], gamma-glutamyl transferase, bilirubin, and albumin) with age, frailty, and survival were investigated in 1,673 community-dwelling men aged 70 years or older. ALT was lower in older participants. Those participants with ALT below the median at baseline had reduced survival (hazard ratio 2.10, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.53-2.87) up to 4.9 years. Older age, frailty, low albumin, low body mass index, and alcohol abstinence also were associated with reduced survival, with age and frailty being the most powerful predictors. Low ALT was associated with frailty (odds ratio 3.54, 95% CI 2.45-5.11), and the relationship between ALT and survival disappeared once frailty and age were included in the survival analysis. Low ALT activity is a predictor of reduced survival; however, this seems to be mediated by its association with frailty and increasing age. ALT has potential value as a novel biomarker of aging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low Alanine Aminotransferase Levels in the Elderly Population: Frailty, Disability, Sarcopenia, and Reduced Survival.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018 Jun 14;73(7):925-930. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx126. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 28633440 Free PMC article.
-
The association between frailty biomarkers and 20-year all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among community-dwelling older adults.Postgrad Med. 2024 Aug;136(6):641-650. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2024.2374703. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Postgrad Med. 2024. PMID: 38940517
-
Physical frailty and mortality risk in Japanese older adults.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018 Jul;18(7):1085-1092. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13316. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018. PMID: 29608043
-
Baseline low ALT activity is associated with increased long-term mortality after COPD exacerbations.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 May 11;20(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1169-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 32393221 Free PMC article.
-
The risks of biomarker-based epidemiology: Associations of circulating calcium levels with age, mortality, and frailty vary substantially across populations.Exp Gerontol. 2018 Jul 1;107:11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Jul 16. Exp Gerontol. 2018. PMID: 28723411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarker-based score to predict mortality in persons aged 50 years and older: a new approach in the Swedish AMORIS study.Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2012;3(1):66-76. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2012. PMID: 22493753 Free PMC article.
-
Low ALT Levels Associated with Poor Outcomes in 8700 Hospitalized Heart Failure Patients.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 30;9(10):3185. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103185. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33008125 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 Polymorphisms and Serum-Induced SIRT1 Protein Expression in Aging and Frailty: The CHAMP Study.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017 Jul 1;72(7):870-876. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx018. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28329314 Free PMC article.
-
Complex association between alanine aminotransferase activity and mortality in general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 14;9(3):e91410. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091410. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24633141 Free PMC article.
-
Low ALT Levels Independently Associated with 22-Year All-Cause Mortality Among Coronary Heart Disease Patients.J Gen Intern Med. 2016 Feb;31(2):209-214. doi: 10.1007/s11606-015-3480-6. Epub 2015 Aug 6. J Gen Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 26245731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marchesini G, Moscatiello S, Di Domizio S, Forlani G. Obesity-associated liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:S74–S80. - PubMed
-
- Chapman IM. Obesity in old age. Front Horm Res. 2008;36:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Elinav E, Ackerman Z, Maaravi Y, Ben-Dov IZ, Ein-Mor E, Stessman J. Low alanine aminotransferase activity in older people is associated with greater long-term mortality. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:1719–1724. - PubMed
-
- Schmucker DL. Age-related changes in liver structure and function: implications for disease? Exp Gerontol. 2005;40:650–659. - PubMed
-
- McLean AJ, Le Couteur DG. Aging biology and geriatric clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:163–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

