CD4 T-cell suppression by cells from Toxoplasma gondii-infected retinas is mediated by surface protein PD-L1
- PMID: 20498261
- PMCID: PMC2916285
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00117-10
CD4 T-cell suppression by cells from Toxoplasma gondii-infected retinas is mediated by surface protein PD-L1
Abstract
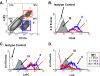
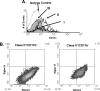
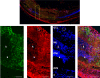
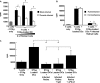
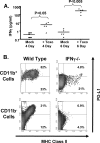
In the inflamed retina, CD4(+) T cells can cause retinal damage when they are not properly regulated. Since tissue expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II and costimulatory molecules is a key mechanism for regulating effector T cells, we tested the hypothesis that upregulation of these proteins in the retina contributes to the regulation of CD4 T cells. Here we report that in retinas infected with the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii, MHC class II is upregulated on infiltrating leukocytes as well as on resident retinal cells, including photoreceptors. Flow cytometric analysis indicated that B7 costimulatory family members (CD80, CD86, ICOS-L, and programmed death ligand 2 [PD-L2]) were not expressed on class II(+) cells. In contrast, PD-L1 (also named B7-H1 or CD274) was expressed on the majority of both hematopoietic and resident retinal MHC class II-expressing cells. Retinal cells from Toxoplasma-infected animals were able to suppress T-cell activation in a PD-L1-dependent manner. Finally, we demonstrate that the expression of MHC class II and PD-L1 was critically dependent on gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) expression. These data suggest that retinal MHC class II and PD-L1 expression is a novel mechanism by which the retina protects itself from CD4 T-cell-mediated immune damage in ocular toxoplasmosis and other types of retinal immune responses.
Figures


References
-
- Blasius, A. L., E. Giurisato, M. Cella, R. D. Schreiber, A. S. Shaw, and M. Colonna. 2006. Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 is a specific marker of type I IFN-producing cells in the naive mouse, but a promiscuous cell surface antigen following IFN stimulation. J. Immunol. 177:3260-3265. - PubMed
-
- Bliss, S. K., B. A. Butcher, and E. Y. Denkers. 2000. Rapid recruitment of neutrophils containing prestored IL-12 during microbial infection. J. Immunol. 165:4515-4521. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, C., P. Knupfer, G. Boush, R. Gausas, and J. Chandler. 1990. In vivo induction of Ia expression in murine cornea after intravitreal injection of interferon-gamma. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 31:2248-2253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI084570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI41930/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI091461/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041930/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI048097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI078993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- EY016459/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI078993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY016459/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- AI078993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI073142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI048097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- A069986/PHS HHS/United States
- R21 AI075931/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

