RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation patterns in Caenorhabditis elegans operons, polycistronic gene clusters with only one promoter
- PMID: 20498277
- PMCID: PMC2916409
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00325-10
RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation patterns in Caenorhabditis elegans operons, polycistronic gene clusters with only one promoter
Abstract
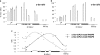
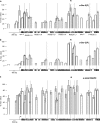
The heptad repeat of the RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) C-terminal domain is phosphorylated at serine 5 near gene 5' ends and serine 2 near 3' ends in order to recruit pre-mRNA processing factors. Ser-5(P) is associated with gene 5' ends to recruit capping enzymes, whereas Ser-2(P) is associated with gene 3' ends to recruit cleavage and polyadenylation factors. In the gene clusters called operons in Caenorhabditis elegans, there is generally only a single promoter, but each gene in the operon forms a 3' end by the usual mechanism. Although downstream operon genes have 5' ends, they receive their caps by trans splicing rather than by capping enzymes. Thus, they are predicted to not need Ser-5 phosphorylation. Here we show by RNAPII chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) that internal operon gene 5' ends do indeed lack Ser-5(P) peaks. In contrast, Ser-2(P) peaks occur at each mRNA 3' end, where the 3'-end formation machinery binds. These results provide additional support for the idea that the serine phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain (CTD) serves to bring RNA-processing enzymes to the transcription complex. Furthermore, these results provide a novel demonstration that genes in operons are cotranscribed from a single upstream promoter.
Figures
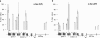
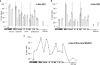
Similar articles
-
Localization of RNAPII and 3' end formation factor CstF subunits on C. elegans genes and operons.Transcription. 2016 May 26;7(3):96-110. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2016.1168509. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Transcription. 2016. PMID: 27124504 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between 3' end formation and SL2-specific trans-splicing in polycistronic Caenorhabditis elegans pre-mRNA processing.RNA. 1997 Mar;3(3):269-78. RNA. 1997. PMID: 9056764 Free PMC article.
-
A global analysis of C. elegans trans-splicing.Genome Res. 2011 Feb;21(2):255-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.113811.110. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21177958 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-splicing and operons in C. elegans.WormBook. 2012 Nov 20:1-11. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.5.2. WormBook. 2012. PMID: 23175478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trans-splicing and operons.WormBook. 2005 Jun 25:1-9. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.5.1. WormBook. 2005. PMID: 18050426 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H3K9 and H4 Acetylations and Transcription Facilitate the Initial CENP-AHCP-3 Deposition and De Novo Centromere Establishment in Caenorhabditis elegans Artificial Chromosomes.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Apr 13;11(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0185-1. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 29653589 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling mRNA processing with transcription in time and space.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Mar;15(3):163-75. doi: 10.1038/nrg3662. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24514444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3' end formation of pre-mRNA and phosphorylation of Ser2 on the RNA polymerase II CTD are reciprocally coupled in human cells.Genes Dev. 2014 Feb 15;28(4):342-56. doi: 10.1101/gad.231274.113. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24478330 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II transcription elongation and Pol II CTD Ser2 phosphorylation: A tail of two kinases.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):224-36. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29347. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24879308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression in C. elegans.WormBook. 2013 Jun 4:1-34. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.45.2. WormBook. 2013. PMID: 23801596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allison, L. A., J. K. Wong, V. D. Fitzpatrick, M. Moyle, and C. J. Ingles. 1988. The C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Drosophila melanogaster, and mammals: a conserved structure with an essential function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:321-329. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baugh, L. R., J. Demodena, and P. W. Sternberg. 2009. RNA Pol II accumulates at promoters of growth genes during developmental arrest. Science 324:92-94. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal, T. 2005. Trans-splicing and operons. WormBook 2005:1-9. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal, T., D. Evans, C. D. Link, A. Guffanti, D. Lawson, J. Thierry-Mieg, D. Thierry-Mieg, W. L. Chiu, K. Duke, M. Kiraly, and S. K. Kim. 2002. A global analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans operons. Nature 417:851-854. - PubMed
-
- Chapman, R. D., M. Heidemann, T. K. Albert, R. Mailhammer, A. Flatley, M. Meisterernst, E. Kremmer, and D. Eick. 2007. Transcribing RNA polymerase II is phosphorylated at CTD residue serine-7. Science 318:1780-1782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
