Profiling of histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation levels predicts transcription factor activity and survival in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 20498303
- PMCID: PMC2981478
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-240978
Profiling of histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation levels predicts transcription factor activity and survival in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
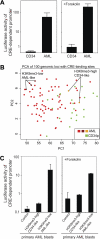
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is commonly associated with alterations in transcription factors because of altered expression or gene mutations. These changes might induce leukemia-specific patterns of histone modifications. We used chromatin-immunoprecipitation on microarray to analyze histone 3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) patterns in primary AML (n = 108), acute lymphoid leukemia (n = 28), CD34(+) cells (n = 21) and white blood cells (n = 15) specimens. Hundreds of promoter regions in AML showed significant alterations in H3K9me3 levels. H3K9me3 deregulation in AML occurred preferentially as a decrease in H3K9me3 levels at core promoter regions. The altered genomic regions showed an overrepresentation of cis-binding sites for ETS and cyclic adenosine monophosphate response elements (CREs) for transcription factors of the CREB/CREM/ATF1 family. The decrease in H3K9me3 levels at CREs was associated with increased CRE-driven promoter activity in AML blasts in vivo. AML-specific H3K9me3 patterns were not associated with known cytogenetic abnormalities. But a signature derived from H3K9me3 patterns predicted event-free survival in AML patients. When the H3K9me3 signature was combined with established clinical prognostic markers, it outperformed prognosis prediction based on clinical parameters alone. These findings demonstrate widespread changes of H3K9me3 levels at gene promoters in AML. Signatures of histone modification patterns are associated with patient prognosis in AML.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Loss of H3K27 methylation identifies poor outcomes in adult-onset acute leukemia.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Jan 28;13(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01011-x. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33509276 Free PMC article.
-
Signatures of polycomb repression and reduced H3K4 trimethylation are associated with p15INK4b DNA methylation in AML.Blood. 2010 Apr 15;115(15):3098-108. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-233858. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20190193 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed genes are marked by histone 3 lysine 9 trimethylation in human cancer cells.Oncogene. 2008 Apr 10;27(17):2412-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210895. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 17968314
-
The Emerging Role of H3K9me3 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2019 Aug 2;9:705. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00705. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31428579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Biological properties and sensitivity to induction therapy of differentiated cells expressing atypical immunophenotype in acute leukemia of children].Folia Med Cracov. 2001;42(3):5-80. Folia Med Cracov. 2001. PMID: 12353422 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The Significance of Modified Histone H3 in Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Cancer.Int Dent J. 2024 Aug;74(4):769-776. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.01.011. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Int Dent J. 2024. PMID: 38326164 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation in cancer progression.Cell Biosci. 2014 Aug 19;4:45. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-4-45. eCollection 2014. Cell Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25949794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JMJD1A, H3K9me1, H3K9me2 and ADM expression as prognostic markers in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 28;13(3):e0194884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194884. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29590186 Free PMC article.
-
Histone trimethylation at H3K4, H3K9 and H4K20 correlates with patient survival and tumor recurrence in early-stage colon cancer.BMC Cancer. 2014 Jul 22;14:531. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-531. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25047223 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic distortion to VDR transcriptional regulation in prostate cancer cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Jul;136:258-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Oct 23. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23098689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Estey E, Dohner H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2006;368(9550):1894–1907. - PubMed
-
- Marcucci G, Mrozek K, Bloomfield CD. Molecular heterogeneity and prognostic biomarkers in adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics. Curr Opin Hematol. 2005;12(1):68–75. - PubMed
-
- Laslo P, Spooner CJ, Warmflash A, et al. Multilineage transcriptional priming and determination of alternate hematopoietic cell fates. Cell. 2006;126(4):755–766. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbauer F, Wagner K, Kutok JL, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia induced by graded reduction of a lineage-specific transcription factor, PU.1. Nat Genet. 2004;36(6):624–630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

