Phase III, placebo-controlled trial of three doses of citalopram for the treatment of hot flashes: NCCTG trial N05C9
- PMID: 20498389
- PMCID: PMC2903326
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.6379
Phase III, placebo-controlled trial of three doses of citalopram for the treatment of hot flashes: NCCTG trial N05C9
Abstract
Purpose: Up to 75% of women experience hot flashes, which can negatively impact quality of life. As hot flash physiology is not definitively understood, it cannot be assumed that effective agents represent class effects. Therefore, there is a continued need for rigorous evaluation to identify effective nonhormonal options for hot flash relief.
Methods: A randomized, double-blind trial evaluated citalopram at target doses of 10, 20, or 30 mg/d versus placebo for 6 weeks. Postmenopausal women with at least 14 bothersome hot flashes per week recorded hot flashes for 7 days before starting treatment and were then titrated to their target doses. The primary end point was the change from baseline to 6 weeks in hot flash score.
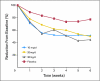
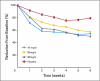
Results: Two hundred fifty-four women were randomly assigned onto this study. Data for hot flash scores and frequencies showed significant improvement in hot flashes with citalopram over placebo, with no significant differences among doses. Reductions in mean hot flash scores were 2.0 (23%), 7.0 (49%), 7.7 (50%), and 10.7 (55%) for placebo and 10, 20, and 30 mg of citalopram, respectively (P <or= .002). Improvement in secondary outcomes, such as the Hot Flash Related Daily Interference Scale, was statistically superior in the 20-mg arm. Citalopram was well-tolerated, with no significant negative adverse effects.
Conclusion: Citalopram is an effective, well-tolerated agent in managing hot flashes. There does not appear to be a significant dose response above 10 mg/d, but broader helpful effects of the agent appear to be more evident at 20 mg/d.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Citalopram for hot flashes.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010 Sep;6(9):475. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.116. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20803805 No abstract available.
-
Climacteric commentaries. The search for an effective non-hormonal treatment for hot flushes continues.Climacteric. 2010 Oct;13(5):504-5. Climacteric. 2010. PMID: 20815102 No abstract available.
References
-
- Carpenter JS, Andrykowski MA. Menopausal symptoms in breast cancer survivors. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1999;26:1311–1317. - PubMed
-
- Couzi RJ HK, Fetting JH. Prevalence of menopausal symptoms among women with a history of breast cancer and attitudes toward estrogen replacement therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:2737–2744. - PubMed
-
- Gracia CR, Freeman EW. Acute consequences of the menopausal transition: The rise of common menopausal symptoms. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004;33:675–689. - PubMed
-
- Stearns V, Ullmer L, Lopez JF, et al. Hot flushes. Lancet. 2002;360:1851–1861. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter JS, Johnson D, Wagner L, et al. Hot flashes and related outcomes in breast cancer survivors and matched comparison women. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2002;29:E16–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA-37404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA124477/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-25224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 124477/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials