Inhibitory effect of CXC chemokine receptor 4 antagonist AMD3100 on bleomycin induced murine pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 20498529
- PMCID: PMC2892600
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2010.42.6.048
Inhibitory effect of CXC chemokine receptor 4 antagonist AMD3100 on bleomycin induced murine pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
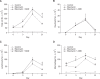
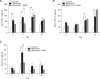
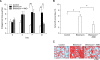
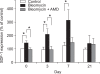
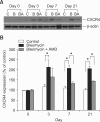
CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), which binds the stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), has been shown to play a critical role in mobilizing the bone marrow (BM)-derived stem cells and inflammatory cells. We studied the effects of AMD3100, CXCR4 antagonist, on a murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis model. Treatment of mice with AMD3100 in bleomycin-treated mice resulted in the decrease of SDF-1 in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids at an early stage and was followed by the decrease of fibrocytes in the lung. AMD3100 treatment decreased the SDF-1 mRNA expression, fibrocyte numbers in the lung at an early stage (day 3) and CXCR4 expression at the later stage (day 7 and 21) after bleomycin injury. The collagen content and pulmonary fibrosis were significantly attenuated by AMD3100 treatment in later stage of bleomycin injury. AMD3100 treatment also decreased the murine mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cell chemotaxis when either in the stimulation with bleomycin treated lung lysates or SDF-1 in vitro. In BM stem cell experiments, the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK which was induced by SDF-1 was significantly blocked by addition of AMD3100. Our data suggest that AMD3100 might be effective in preventing the pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the fibrocyte mobilization to the injured lung via blocking the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis.
Figures

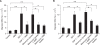
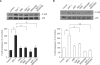
References
-
- Abe R, Donnelly SC, Peng T, Bucala R, Metz CN. Peripheral blood fibrocytes: differentiation pathway and migration to wound sites. J Immunol. 2001;166:7556–7562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
