Pdcd4 repression of lysyl oxidase inhibits hypoxia-induced breast cancer cell invasion
- PMID: 20498644
- PMCID: PMC3419530
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.158
Pdcd4 repression of lysyl oxidase inhibits hypoxia-induced breast cancer cell invasion
Abstract
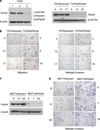
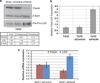
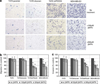
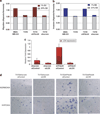
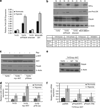
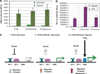
Metastasis to bone, liver and lungs is the primary cause of death in breast cancer patients. Our studies have revealed that the novel tumor suppressor Pdcd4 inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro. Loss of Pdcd4 in human nonmetastatic breast cancer cells increased the expression of lysyl oxidase (LOX) mRNA. LOX is a hypoxia-inducible amine oxidase, the activity of which enhances breast cancer cell invasion in vitro and in vivo. Specific inhibition of LOX activity by beta-aminopropionitrile or small interfering RNA decreased the invasiveness of T47D and MCF7 breast cancer cells attenuated for Pdcd4 function. Most significantly, loss of Pdcd4 augments hypoxia induction of LOX as well. Conversely, overexpression of Pdcd4 significantly reversed the hypoxia induction of LOX expression in T47D cells attenuated for Pdcd4. However, Pdcd4 did not affect hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) protein expression or HIF-1-responsive element-luciferase activity in response to hypoxia, suggesting that Pdcd4 regulation of LOX occurs through an HIF-independent mechanism. Nevertheless, the loss of Pdcd4 early in cancer progression may have an important role in the increased sensitivity of cancer cells to hypoxia through increased LOX activity and concomitant enhanced invasiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia/reoxygenation: a dynamic regulator of lysyl oxidase-facilitated breast cancer migration.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Apr 1;103(5):1369-78. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21517. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17685448
-
Hypoxia inducible factor 1α-mediated LOX expression correlates with migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer.Int J Oncol. 2013 May;42(5):1578-88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1878. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23545606 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2R activation by nucleotides released from the highly metastatic breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 contributes to pre-metastatic niche formation by mediating lysyl oxidase secretion, collagen crosslinking, and monocyte recruitment.Oncotarget. 2014 Oct 15;5(19):9322-34. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2427. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25238333 Free PMC article.
-
Lysyl oxidase (LOX) and hypoxia-induced metastases.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Aug;5(8):909-11. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.8.3230. Epub 2006 Aug 26. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16969095 Review.
-
Lysyl Oxidase, a Targetable Secreted Molecule Involved in Cancer Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 15;76(2):188-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2306. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26732355 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic interplay between the collagen scaffold and tumor evolution.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;22(5):697-706. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.08.015. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20822891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Pdcd4 in tumour suppression and protein translation.Biol Cell. 2018 May 28:10.1111/boc.201800014. doi: 10.1111/boc.201800014. Online ahead of print. Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29806708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pdcd4 knockdown up-regulates MAP4K1 expression and activation of AP-1 dependent transcription through c-Myc.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Oct;1823(10):1807-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22801218 Free PMC article.
-
circ-NOL10 regulated by MTDH/CASC3 inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis via multiple miRNAs and PDCD4.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Oct 1;26:773-786. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.09.013. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34729247 Free PMC article.
-
P-selectin-mediated LOX expression promotes insulinoma growth in Rip1-Tag2 mice by increasing tissue stiffness.Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Oct 18;12(11):1289-1297. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.16405. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27877081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arsham AM, Plas DR, Thompson CB, Simon MC. Akt and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 independently enhance tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3500–3507. - PubMed
-
- Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:2128–2136. - PubMed
-
- Bedogni B, Welford SM, Cassarino DS, Nickoloff BJ, Giaccia AJ, Powell MB. The hypoxic microenvironment of the skin contributes to Akt-mediated melanocyte transformation. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:443–454. - PubMed
-
- Bitomsky N, Bohm M, Klempnauer KH. Transformation suppressor protein Pdcd4 interferes with JNK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Jun and recruitment of the coactivator p300 by c-Jun. Oncogene. 2004;23:7484–7493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

