A single immunization with soluble recombinant trimeric hemagglutinin protects chickens against highly pathogenic avian influenza virus H5N1
- PMID: 20498717
- PMCID: PMC2871037
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010645
A single immunization with soluble recombinant trimeric hemagglutinin protects chickens against highly pathogenic avian influenza virus H5N1
Abstract
Background: The highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus H5N1 causes multi-organ disease and death in poultry, resulting in significant economic losses in the poultry industry. In addition, it poses a major public health threat as it can be transmitted directly from infected poultry to humans with very high (60%) mortality rate. Effective vaccination against HPAI H5N1 would protect commercial poultry and would thus provide an important control measure by reducing the likelihood of bird-to-bird and bird-to-human transmission.
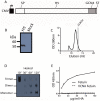
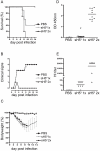
Methodology/principal findings: In the present study we evaluated the vaccine potential of recombinant soluble trimeric subtype 5 hemagglutinin (sH5(3)) produced in mammalian cells. The secreted, purified sH5(3) was biologically active as demonstrated by its binding to ligands in a sialic acid-dependent manner. It was shown to protect chickens, in a dose-dependent manner, against a lethal challenge with H5N1 after a single vaccination. Protected animals did not shed challenge virus as determined by a quantitative RT-PCR on RNA isolated from trachea and cloaca swabs. Also in mice, vaccination with sH5(3) provided complete protection against challenge with HPAI H5N1.
Conclusions/significance: Our results demonstrate that sH5(3) constitutes an attractive vaccine antigen for protection of chickens and mammals against HPAI H5N1. As these recombinant soluble hemagglutinin preparations can be produced with high yields and with relatively short lead time, they enable a rapid response to circulating and potentially pandemic influenza viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Munster VJ, Fouchier RA. Avian influenza virus: of virus and bird ecology. Vaccine. 2009;27:6340–6344. - PubMed
-
- Uyeki TM. Global epidemiology of human infections with highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) viruses. Respirology. 2008;13(Suppl 1):S2–9. - PubMed
-
- Yen HL, Webster RG. Pandemic influenza as a current threat. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;333:3–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

