Synthesis of 5-hydroxyectoine from ectoine: crystal structure of the non-heme iron(II) and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase EctD
- PMID: 20498719
- PMCID: PMC2871039
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010647
Synthesis of 5-hydroxyectoine from ectoine: crystal structure of the non-heme iron(II) and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase EctD
Abstract
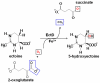
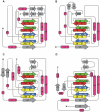
As a response to high osmolality, many microorganisms synthesize various types of compatible solutes. These organic osmolytes aid in offsetting the detrimental effects of low water activity on cell physiology. One of these compatible solutes is ectoine. A sub-group of the ectoine producer's enzymatically convert this tetrahydropyrimidine into a hydroxylated derivative, 5-hydroxyectoine. This compound also functions as an effective osmostress protectant and compatible solute but it possesses properties that differ in several aspects from those of ectoine. The enzyme responsible for ectoine hydroxylation (EctD) is a member of the non-heme iron(II)-containing and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases (EC 1.14.11). These enzymes couple the decarboxylation of 2-oxoglutarate with the formation of a high-energy ferryl-oxo intermediate to catalyze the oxidation of the bound organic substrate. We report here the crystal structure of the ectoine hydroxylase EctD from the moderate halophile Virgibacillus salexigens in complex with Fe(3+) at a resolution of 1.85 A. Like other non-heme iron(II) and 2-oxoglutarate dependent dioxygenases, the core of the EctD structure consists of a double-stranded beta-helix forming the main portion of the active-site of the enzyme. The positioning of the iron ligand in the active-site of EctD is mediated by an evolutionarily conserved 2-His-1-carboxylate iron-binding motif. The side chains of the three residues forming this iron-binding site protrude into a deep cavity in the EctD structure that also harbours the 2-oxoglutarate co-substrate-binding site. Database searches revealed a widespread occurrence of EctD-type proteins in members of the Bacteria but only in a single representative of the Archaea, the marine crenarchaeon Nitrosopumilus maritimus. The EctD crystal structure reported here can serve as a template to guide further biochemical and structural studies of this biotechnologically interesting enzyme family.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
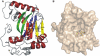
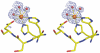
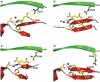
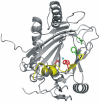
Similar articles
-
Molecular dynamics simulations and structure-guided mutagenesis provide insight into the architecture of the catalytic core of the ectoine hydroxylase.J Mol Biol. 2014 Feb 6;426(3):586-600. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.028. Epub 2013 Oct 30. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24184278
-
Crystal structure of the ectoine hydroxylase, a snapshot of the active site.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 24;289(43):29570-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.576769. Epub 2014 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25172507 Free PMC article.
-
Osmotically induced synthesis of the compatible solute hydroxyectoine is mediated by an evolutionarily conserved ectoine hydroxylase.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 26;282(43):31147-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704023200. Epub 2007 Jul 18. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17636255
-
Catalytic Mechanisms of Fe(II)- and 2-Oxoglutarate-dependent Oxygenases.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 21;290(34):20702-20711. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.648691. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26152721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural studies on 2-oxoglutarate oxygenases and related double-stranded beta-helix fold proteins.J Inorg Biochem. 2006 Apr;100(4):644-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2006.01.024. Epub 2006 Mar 2. J Inorg Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16513174 Review.
Cited by
-
Fe(2)OG: an integrated HMM profile-based web server to predict and analyze putative non-haem iron(II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase function in protein sequences.BMC Res Notes. 2021 Mar 1;14(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13104-021-05477-z. BMC Res Notes. 2021. PMID: 33648553 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical properties of ectoine hydroxylases from extremophiles and their wider taxonomic distribution among microorganisms.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 8;9(4):e93809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093809. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24714029 Free PMC article.
-
Rational engineering of Halomonas salifodinae to enhance hydroxyectoine production under lower-salt conditions.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 May 31;108(1):353. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13197-0. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38819481 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative cyclizations in orthosomycin biosynthesis expand the known chemistry of an oxygenase superfamily.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 15;112(37):11547-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500964112. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26240321 Free PMC article.
-
Glass-forming property of hydroxyectoine is the cause of its superior function as a desiccation protectant.Front Microbiol. 2014 Apr 4;5:150. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00150. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24772110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Booth IR, Edwards MD, Black S, Schumann U, Miller S. Mechanosensitive channels in bacteria: signs of closure? Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Bremer E, Krämer R. Storz G, Hengge-Aronis R, editors. Coping with osmotic challenges:osmoregulation through accumulation and release of compatible solutes in bacteria. Bacterial stress responses. 2000. pp. 79–97. Washington, DC, USA ASM Press.
-
- Kempf B, Bremer E. Uptake and synthesis of compatible solutes as microbial stress responses to high-osmolality environments. Arch Microbiol. 1998;170:319–330. - PubMed
-
- da Costa MS, Santos H, Galinski EA. An overview of the role and diversity of compatible solutes in Bacteria and Archaea. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 1998;61:117–153. - PubMed
-
- Bursy J, Pierik AJ, Pica N, Bremer E. Osmotically induced synthesis of the compatible solute hydroxyectoine is mediated by an evolutionarily conserved ectoine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:31147–31155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

