Increased friction coefficient and superficial zone protein expression in patients with advanced osteoarthritis
- PMID: 20499384
- PMCID: PMC2946421
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27577
Increased friction coefficient and superficial zone protein expression in patients with advanced osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: To quantify the concentration of superficial zone protein (SZP) in the articular cartilage and synovial fluid of patients with advanced osteoarthritis (OA) and to further correlate the SZP content with the friction coefficient, OA severity, and levels of proinflammatory cytokines.
Methods: Samples of articular cartilage and synovial fluid were obtained from patients undergoing elective total knee replacement surgery. Additional normal samples were obtained from donated body program and tissue bank sources. Regional SZP expression in cartilage obtained from the femoral condyles was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and visualized by immunohistochemistry. Friction coefficient measurements of cartilage plugs slid in the boundary lubrication system were obtained. OA severity was graded using histochemical analyses. The concentrations of SZP and proinflammatory cytokines in synovial fluid were determined by ELISA.
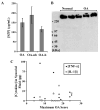
Results: A pattern of SZP localization in knee cartilage was identified, with load-bearing regions exhibiting high SZP expression. SZP expression patterns were correlated with friction coefficient and OA severity; however, SZP expression was observed in all samples at the articular surface, regardless of OA severity. SZP expression and aspirate volume of synovial fluid were higher in OA patients than in normal controls. Expression of cytokines was elevated in the synovial fluid of some patients.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate a mechanochemical coupling in which physical forces regulate OA severity and joint lubrication. The findings of this study also suggest that SZP may be ineffective in reducing joint friction in the boundary lubrication mode at an advanced stage of OA, where other mechanisms may dominate the observed tribological behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanotransduction of bovine articular cartilage superficial zone protein by transforming growth factor beta signaling.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Nov;56(11):3706-14. doi: 10.1002/art.23024. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17968924
-
Stimulation of the superficial zone protein and lubrication in the articular cartilage by human platelet-rich plasma.Am J Sports Med. 2015 Jun;43(6):1467-73. doi: 10.1177/0363546515575023. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Am J Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 25813869 Free PMC article.
-
Diminished cartilage-lubricating ability of human osteoarthritic synovial fluid deficient in proteoglycan 4: Restoration through proteoglycan 4 supplementation.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Dec;64(12):3963-71. doi: 10.1002/art.34674. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22933061
-
Recent Advances in Understanding the Role of Cartilage Lubrication in Osteoarthritis.Molecules. 2021 Oct 11;26(20):6122. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206122. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of interstitial fluid pressurization in articular cartilage lubrication.J Biomech. 2009 Jun 19;42(9):1163-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.04.040. Epub 2009 May 22. J Biomech. 2009. PMID: 19464689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tailoring hydrogel surface properties to modulate cellular response to shear loading.Acta Biomater. 2017 Apr 1;52:105-117. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27729233 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of a gelatin β-tricalcium phosphate sponge loaded with mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), bone morphogenic protein-2, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on equine articular cartilage defect.Can Vet J. 2013 Jun;54(6):573-80. Can Vet J. 2013. PMID: 24155448 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Stimulation of Superficial Zone Protein/Lubricin/PRG4 by Transforming Growth Factor-β in Superficial Zone Articular Chondrocytes and Modulation by Glycosaminoglycans.Tissue Eng Part A. 2015 Jul;21(13-14):1973-81. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2014.0381. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015. PMID: 25398329 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of histologically scored human knee osteochondral plugs by quantitative analysis of magnetic resonance images at 3T.J Orthop Res. 2015 May;33(5):640-50. doi: 10.1002/jor.22810. Epub 2015 Mar 5. J Orthop Res. 2015. PMID: 25641500 Free PMC article.
-
Does intra-articular fracture change the lubricant content of synovial fluid?J Orthop Surg Res. 2015 Jun 3;10:89. doi: 10.1186/s13018-015-0232-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 26037740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schumacher BL, Block JA, Schmid TM, Aydelotte MB, Kuettner KE. A novel proteoglycan synthesized and secreted by chondrocytes of the superficial zone of articular cartilage. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;311(1):144–52. - PubMed
-
- Neu CP, Khalafi A, Komvopoulos K, Schmid T, Reddi AH. Mechanotransduction of bovine articular cartilage superficial zone protein by transforming growth factor β signaling. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(11):3706–14. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence RC, Helmick CG, Arnett FC, Deyo RA, Felson DT, Giannini EH, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and selected musculoskeletal disorders in the United States. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(5):778–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

