Importance of replication in analyzing time-series gene expression data: corticosteroid dynamics and circadian patterns in rat liver
- PMID: 20500897
- PMCID: PMC2889936
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-279
Importance of replication in analyzing time-series gene expression data: corticosteroid dynamics and circadian patterns in rat liver
Abstract
Background: Microarray technology is a powerful and widely accepted experimental technique in molecular biology that allows studying genome wide transcriptional responses. However, experimental data usually contain potential sources of uncertainty and thus many experiments are now designed with repeated measurements to better assess such inherent variability. Many computational methods have been proposed to account for the variability in replicates. As yet, there is no model to output expression profiles accounting for replicate information so that a variety of computational models that take the expression profiles as the input data can explore this information without any modification.
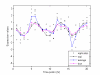
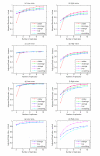
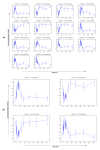
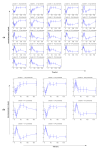
Results: We propose a methodology which integrates replicate variability into expression profiles, to generate so-called 'true' expression profiles. The study addresses two issues: (i) develop a statistical model that can estimate 'true' expression profiles which are more robust than the average profile, and (ii) extend our previous micro-clustering which was designed specifically for clustering time-series expression data. The model utilizes a previously proposed error model and the concept of 'relative difference'. The clustering effectiveness is demonstrated through synthetic data where several methods are compared. We subsequently analyze in vivo rat data to elucidate circadian transcriptional dynamics as well as liver-specific corticosteroid induced changes in gene expression.
Conclusions: We have proposed a model which integrates the error information from repeated measurements into the expression profiles. Through numerous synthetic and real time-series data, we demonstrated the ability of the approach to improve the clustering performance and assist in the identification and selection of informative expression motifs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of acute and chronic corticosteroid pharmacogenomic effects in rat liver: transcriptional dynamics and regulatory structures.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Oct 14;11:515. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-515. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20946642 Free PMC article.
-
Information criterion-based clustering with order-restricted candidate profiles in short time-course microarray experiments.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 May 15;10:146. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-146. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19445669 Free PMC article.
-
A mixture model with random-effects components for clustering correlated gene-expression profiles.Bioinformatics. 2006 Jul 15;22(14):1745-52. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl165. Epub 2006 May 3. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16675467
-
From microarray to biological networks: Analysis of gene expression profiles.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;316:35-48. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-964-8:35. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16671399 Review.
-
Functional genomics and proteomics in the clinical neurosciences: data mining and bioinformatics.Prog Brain Res. 2006;158:83-108. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)58004-5. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17027692 Review.
Cited by
-
Extended local similarity analysis (eLSA) of microbial community and other time series data with replicates.BMC Syst Biol. 2011;5 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S15. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-S2-S15. Epub 2011 Dec 14. BMC Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 22784572 Free PMC article.
-
Time Series Transcriptome Analysis in Medicago truncatula Shoot and Root Tissue During Early Nodulation.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 7;13:861639. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.861639. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35463395 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway-Based Analysis of the Liver Response to Intravenous Methylprednisolone Administration in Rats: Acute Versus Chronic Dosing.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2019 Apr 15;13:1177625019840282. doi: 10.1177/1177625019840282. eCollection 2019. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2019. PMID: 31019365 Free PMC article.
-
Deconvolution of the confounding variations for reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction by separate analysis of biological replicate data.Anal Biochem. 2012 Aug 1;427(1):21-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.04.029. Epub 2012 May 2. Anal Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22561916 Free PMC article.
-
Time series expression analyses using RNA-seq: a statistical approach.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:203681. doi: 10.1155/2013/203681. Epub 2013 Mar 24. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23586021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lonnstedt I, Speed T. Replicated microarray data. Statistica Sinica. 2002;12:31–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

