Chronic oxidative stress sensitizes hepatocytes to death from 4-hydroxynonenal by JNK/c-Jun overactivation
- PMID: 20501438
- PMCID: PMC2777462
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00151.2009
Chronic oxidative stress sensitizes hepatocytes to death from 4-hydroxynonenal by JNK/c-Jun overactivation
Abstract
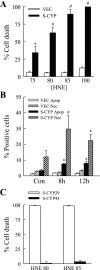
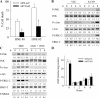
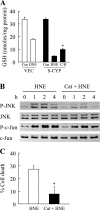
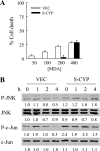
Sustained activation of the c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway mediates the development and progression of experimental diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Delineating the mechanism of JNK overactivation in the setting of a fatty liver is therefore essential to understanding the pathophysiology of NAFLD. Both human and experimental NAFLD are associated with oxidative stress and resultant lipid peroxidation, which have been proposed to mediate the progression of this disease from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis. The ability of oxidants and the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) to activate JNK signaling suggested that these two factors may act synergistically to trigger JNK overactivation. The effect of HNE on hepatocyte injury and JNK activation was therefore examined in cells under chronic oxidant stress from overexpression of the prooxidant enzyme cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1), which occurs in NAFLD. CYP2E1-generated oxidant stress sensitized a rat hepatocyte cell line to death from normally nontoxic concentrations of HNE. CYP2E1-overexpressing cells underwent a more profound depletion of glutathione (GSH) in response to HNE secondary to decreased gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase activity. GSH depletion led to overactivation of JNK/c-Jun signaling at the level of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 that induced cell death. Oxidant stress and the lipid peroxidation product HNE cause synergistic overactivation of the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway in hepatocytes, demonstrating that HNE may not be just a passive biomarker of hepatic oxidant stress but rather an active mediator of hepatocellular injury through effects on JNK signaling.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Increased cytochrome P-450 2E1 expression sensitizes hepatocytes to c-Jun-mediated cell death from TNF-alpha.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002 Feb;282(2):G257-66. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00304.2001. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11804847
-
Activation of stress signaling pathways by the end product of lipid peroxidation. 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal is a potential inducer of intracellular peroxide production.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jan 22;274(4):2234-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.4.2234. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 9890986
-
Apoptosis signalling by 4-hydroxynonenal: a role for JNK-c-Jun/AP-1 pathway.Redox Rep. 2007;12(1):30-4. doi: 10.1179/135100007X162329. Redox Rep. 2007. PMID: 17263905
-
Regulation of the effects of CYP2E1-induced oxidative stress by JNK signaling.Redox Biol. 2014;3:7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.09.004. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 25462060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid peroxidation and cell cycle signaling: 4-hydroxynonenal, a key molecule in stress mediated signaling.Acta Biochim Pol. 2003;50(2):319-36. Acta Biochim Pol. 2003. PMID: 12833161 Review.
Cited by
-
Additive effects of nicotine and high-fat diet on hepatic steatosis in male mice.Endocrinology. 2012 Dec;153(12):5809-20. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1750. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 23093702 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic reticuloendothelial system cell iron deposition is associated with increased apoptosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1806-13. doi: 10.1002/hep.26238. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23325576 Free PMC article.
-
PNPLA3 I148 M genetic variant in autoimmune hepatitis characterises advanced disease at diagnosis and reduced survival free of cirrhotic events and liver-related mortality.J Transl Autoimmun. 2024 Jun 6;9:100243. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2024.100243. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Transl Autoimmun. 2024. PMID: 38974691 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Gsta4 deficiency on age-related cochlear pathology and hearing loss in mice.Exp Gerontol. 2020 May;133:110872. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2020.110872. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Exp Gerontol. 2020. PMID: 32044382 Free PMC article.
-
Additive effects of nicotine and high-fat diet on hepatocellular apoptosis in mice: involvement of caspase 2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase-mediated intrinsic pathway signaling.Horm Metab Res. 2014 Jul;46(8):568-73. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1375610. Epub 2014 May 15. Horm Metab Res. 2014. PMID: 24830635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson ME, Powrie F, Puri RN, Meister A. Glutathione monoethyl ester: preparation, uptake by tissues, and conversion to glutathione. Arch Biochem Biophys 239: 538–548, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Benedetti A, Comporti M, Fulceri R, Esterbauer H. Cytotoxic aldehydes originating from the peroxidation of liver microsomal lipids. Identification of 4,5-dihydroxydecenal. Biochim Biophys Acta 792: 172–181, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Botta D, Shi S, White CC, Dabrowski MJ, Keener CL, Srinouanprachanh SL, Farin FM, Ware CB, Ladiges WC, Pierce RH, Fausto N, Kavanagh TJ. Acetaminophen-induced liver injury is attenuated in male glutamate-cysteine ligase transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 281: 28865–28875, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bradham CA, Hatano E, Brenner DA. Dominant-negative TAK1 induces c-Myc and G0 exit in liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281: G1279–G1289, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bruckner SR, Estus S. JNK3 contributes to c-jun induction and apoptosis in 4-hydroxynonenal-treated sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci Res 70: 665–670, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

