A multimarker approach to assess the influence of inflammation on the incidence of atrial fibrillation in women
- PMID: 20501475
- PMCID: PMC2903714
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq146
A multimarker approach to assess the influence of inflammation on the incidence of atrial fibrillation in women
Abstract
Aims: To assess the joint influence of inflammatory biomarkers on the risk of incident atrial fibrillation (AF) in women.
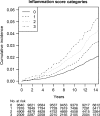
Methods and results: We performed a prospective cohort study among women participating in the Women's Health Study. All women were free of AF at study entry and provided a baseline blood sample assayed for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and fibrinogen. To evaluate the joint effect of these three biomarkers, an inflammation score was created that ranged from 0 to 3 and reflected the number of biomarkers in the highest tertile per individual. During a median follow-up of 14.4 years, 747 of 24,734 women (3.0%) experienced a first AF event. Assessed individually, all three biomarkers were associated with incident AF, even after adjustment for traditional risk factors. When combined into an inflammation score, a strong and independent relationship between inflammation and incident AF emerged. Across increasing inflammation score categories, there were 1.66, 2.22, 2.73, and 3.25 AF events per 1000 person-years of follow-up. The corresponding hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) across inflammation score categories were 1.0, 1.22 (1.00-1.49), 1.32 (1.06-1.65), and 1.59 (1.22-2.06) (P for linear trend 0.0006) after multivariable adjustment.
Conclusion: In this large-scale prospective study among women without a history of cardiovascular disease, markers of systemic inflammation were significantly related to AF even after controlling for traditional risk factors.
Figures
References
-
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, Singer DE. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention. The AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–2375. doi:10.1001/jama.285.18.2370. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miyasaka Y, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Cha SS, Bailey KR, Abhayaratna WP, Seward JB, Tsang TS. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation. 2006;114:119–125. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.595140. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ, Belanger AJ, Kannel WB, Levy D, D'Agostino RB. Secular trends in the prevalence of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Study. Am Heart J. 1996;131:790–795. doi:10.1016/S0002-8703(96)90288-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998;98:946–952. - PubMed
-
- Ott A, Breteler MM, de Bruyne MC, van Harskamp F, Grobbee DE, Hofman A. Atrial fibrillation and dementia in a population-based study. The Rotterdam Study. Stroke. 1997;28:316–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials