Androgen receptor counteracts Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in male mice
- PMID: 20501642
- PMCID: PMC5417461
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0402
Androgen receptor counteracts Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in male mice
Abstract
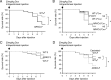
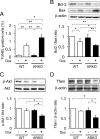
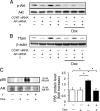
Doxorubicin (Dox) has been used as a potent anticancer agent, but serious cardiotoxicity precludes its use in a wide range of patients. We have reported that the androgen-androgen receptor (AR) system plays important roles in cardiac growth and protection from angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling. The present study was undertaken to clarify whether the androgen-AR system exerts a cardioprotective effect against Dox-induced cardiotoxicity. Male AR knockout (ARKO) and age-matched littermate male wild-type (WT) mice at 25 wk of age were given ip injections of Dox (20 mg/kg) or a vehicle. The survival rate and left ventricular function in Dox-treated male ARKO mice were reduced compared with those in Dox-treated male WT mice. Electron microscopic study showed prominent vacuole formation of myocardial mitochondria in Dox-treated male ARKO mice. Cardiac oxidative stress and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes were increased more prominently by Dox treatment in male ARKO mice than in male WT mice. In addition, Dox-induced reduction in the expression of cardiac mitochondria transcription factor A (Tfam) and phosphorylation of serine-threonine kinase (Akt) was more pronounced in male ARKO mice than in male WT mice. In cardiac myoblast cells, testosterone up-regulated Akt phosphorylation and Tfam expression and exerted an antiapoptotic effect against Dox-induced cardiotoxicity. Collectively, the results demonstrate that Dox-induced cardiotoxicity is aggravated in male ARKO mice via exacerbation of mitochondrial damage and superoxide generation, leading to enhanced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. Thus, the androgen-AR system is thought to counteract Dox-induced cardiotoxicity partly through activation of the Akt pathway and up-regulation of Tfam to protect cardiomyocytes from mitochondrial damage and apoptosis.
Figures



References
-
- Von Hoff DD, Layard MW, Basa P, Davis Jr HL, Von Hoff AL, Rozencweig M, Muggia FM1979. Risk factors for doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann Intern Med 91:710–717 - PubMed
-
- Billingham ME, Mason JW, Bristow MR, Daniels JR1978. Anthracycline cardiomyopathy monitored by morphologic changes. Cancer Treat Rep 62:865–872 - PubMed
-
- Bristow MR, Thompson PD, Martin RP, Mason JW, Billingham ME, Harrison DC1978. Early anthracycline cardiotoxicity. Am J Med 65:823–832 - PubMed
-
- Rajagopalan S, Politi PM, Sinha BK, Myers CE1988. Adriamycin-induced free radical formation in the perfused rat heart: implications for cardiotoxicity. Cancer Res 48:4766–4769 - PubMed
-
- Gupta M, Singal PK1987. Oxygen radical injury in the presence of desferal, a specific iron-chelating agent. Biochem Pharmacol 36:3774–3777 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

