Identification of microRNA-93 as a novel regulator of vascular endothelial growth factor in hyperglycemic conditions
- PMID: 20501654
- PMCID: PMC2906336
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.136168
Identification of microRNA-93 as a novel regulator of vascular endothelial growth factor in hyperglycemic conditions
Abstract
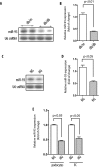
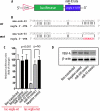
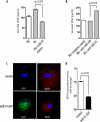
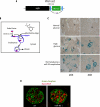
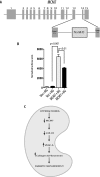
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a dimeric glycoprotein that plays a crucial role in microvascular complications of diabetes, including diabetic nephropathy. However, the precise regulatory mechanisms governing VEGF expression in the diabetic milieu are still poorly understood. Here, we provide evidence that microRNA-93 (miR-93) regulates VEGF expression in experimental models of diabetes both in vitro and in vivo. Comparative microRNA expression profile arrays identified miR-93 as a signature microRNA in hyperglycemic conditions. We identified VEGF-A as a putative target of miR-93 in the kidney with a perfect complementarity between miR-93 and the 3'-untranslated region of vegfa in several species. When cotransfected with a luciferase reporter construct containing the mouse vegfa 3'-untranslated region, expression of miR-93 markedly decreased the luciferase activity. We showed that forced expression of miR-93 in cells abrogated VEGF protein secretion. Conversely, anti-miR-93 inhibitors increased VEGF release. Transfection of miR-93 also prevented the effect of high glucose on VEGF downstream targets. Using transgenic mice containing VEGF-LacZ bicistronic transcripts, we found that inhibition of glomerular miR-93 by peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers elicited increased expression of VEGF. Our findings also indicate that high glucose decreases miR-93 expression by down-regulating the promoter of the host MCM7 gene. Taken together, our findings provide new insights into the role of miR-93 in VEGF signaling pathway and offer a potentially novel target in preventing the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
Figures


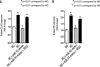
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-29c is a signature microRNA under high glucose conditions that targets Sprouty homolog 1, and its in vivo knockdown prevents progression of diabetic nephropathy.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 1;286(13):11837-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.194969. Epub 2011 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21310958 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-15b-5p shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles protects podocytes from diabetic nephropathy via downregulation of VEGF/PDK4 axis.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2022 Feb;54(1):17-30. doi: 10.1007/s10863-021-09919-y. Epub 2021 Nov 22. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2022. PMID: 34806156
-
MicroRNA-200b regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated alterations in diabetic retinopathy.Diabetes. 2011 Apr;60(4):1314-23. doi: 10.2337/db10-1557. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21357793 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Pathogenesis of Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetic Nephropathy and Retinopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 25;13:816400. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.816400. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35692405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA regulatory networks in post-transcriptional regulation of VEGFA in cancer.IUBMB Life. 2023 Jan;75(1):30-39. doi: 10.1002/iub.2620. Epub 2022 May 10. IUBMB Life. 2023. PMID: 35467790 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs and Risk Factors for Diabetic Nephropathy in Egyptian Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Jul 13;13:2485-2494. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S247062. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32765027 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-RNAs in inflammatory diseases and as a link between inflammation and cancer.Inflamm Res. 2013 Apr;62(4):343-55. doi: 10.1007/s00011-013-0600-9. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Inflamm Res. 2013. PMID: 23417288 Review.
-
microRNA-18b modulates insulin-like growth factor-1 expression in deer antler cell proliferation by directly targeting its 3' untranslated region.DNA Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;34(4):282-9. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2421. Epub 2015 Mar 10. DNA Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25756952 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-93 controls perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia by modulating expression of multiple genes in the cell cycle pathway.Circulation. 2013 Apr 30;127(17):1818-28. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000860. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Circulation. 2013. PMID: 23559675 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance and expression of microRNA in diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Jul;10(1):213-218. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2443. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26170937 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

