Mechanism of radiosensitization by the Chk1/2 inhibitor AZD7762 involves abrogation of the G2 checkpoint and inhibition of homologous recombinational DNA repair
- PMID: 20501833
- PMCID: PMC2889008
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3573
Mechanism of radiosensitization by the Chk1/2 inhibitor AZD7762 involves abrogation of the G2 checkpoint and inhibition of homologous recombinational DNA repair
Abstract
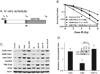
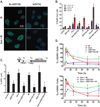
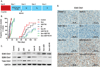
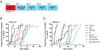
The median survival for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer treated with gemcitabine and radiation is approximately 1 year. To develop improved treatment, we have combined a Chk1/2-targeted agent, AZD7762, currently in phase I clinical trials, with gemcitabine and ionizing radiation in preclinical pancreatic tumor models. We found that in vitro AZD7762 alone or in combination with gemcitabine significantly sensitized MiaPaCa-2 cells to radiation. AZD7762 inhibited Chk1 autophosphorylation (S296 Chk1), stabilized Cdc25A, and increased ATR/ATM-mediated Chk1 phosphorylation (S345 Chk1). Radiosensitization by AZD7762 was associated with abrogation of the G(2) checkpoint as well as with inhibition of Rad51 focus formation, inhibition of homologous recombination repair, and persistent gamma-H2AX expression. AZD7762 was also a radiation sensitizer in multiple tumor xenograft models. In both MiaPaCa-2- and patient-derived xenografts, AZD7762 significantly prolonged the median time required for tumor volume doubling in response to gemcitabine and radiation. Together, our findings suggest that G(2) checkpoint abrogation and homologous recombination repair inhibition both contribute to sensitization by Chk1 inhibition. Furthermore, they support the clinical use of AZD7762 in combination with gemcitabine and radiation for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
L. H.-G., D.M., and S.D.Z. are employees of AstraZeneca.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sensitization of Pancreatic Cancers to Gemcitabine Chemoradiation by WEE1 Kinase Inhibition Depends on Homologous Recombination Repair.Neoplasia. 2015 Oct;17(10):757-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2015.09.006. Neoplasia. 2015. PMID: 26585231 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of chk1 phosphorylation as a pharmacodynamic biomarker of chk1 inhibition.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 1;17(11):3706-15. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3082. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21482692 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo radiation sensitization of human tumor cells by a novel checkpoint kinase inhibitor, AZD7762.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 1;16(7):2076-84. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3277. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20233881 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on the combination of radiotherapy and targeted therapy with DNA repair inhibitors in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 28;22(32):7275-88. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i32.7275. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27621574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer therapy with checkpoint inhibitors: what, where and when?Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011 May;32(5):308-16. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.02.014. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21458083 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting mcl-1 for radiosensitization of pancreatic cancers.Transl Oncol. 2015 Feb;8(1):47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2014.12.004. Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25749177 Free PMC article.
-
Selective tumor killing based on specific DNA-damage response deficiencies.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Mar;13(5):239-46. doi: 10.4161/cbt.18921. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22258411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA double-strand break repair as determinant of cellular radiosensitivity to killing and target in radiation therapy.Front Oncol. 2013 May 10;3:113. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00113. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23675572 Free PMC article.
-
PARP and CHK inhibitors interact to cause DNA damage and cell death in mammary carcinoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 May;14(5):458-65. doi: 10.4161/cbt.24424. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23917378 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of hypoxia-activated prodrug TH-302 anti-tumor activity by Chk1 inhibition.BMC Cancer. 2015 May 21;15:422. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1387-6. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25994202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ries LAG, Melbert DKM, Stinchcomb DG, Howlader N, Horner MJ, Mariotto A, Miller BA, Feuer EJ, Altekruse SF, Lewis DR, Clegg L, Eisner MP, Reichman M, Edwards BK, editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2005. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2008.
-
- Loehrer PJ, Powell ME, Cardenes HR, et al. A randomized phase III study of gemcitabine in combination with radiation therapy versus gemcitabine alone in patients with localized, unresectable pancreatic cancer: E4201. J Clin Oncol. 2008 May;20(suppl):4506. ASCO Meeting Abstracts.
-
- McGinn CJ, Zalupski MM, Shureiqi I, et al. Phase I trial of radiation dose escalation with concurrent weekly full-dose gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(22):4202–4208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

