Identification of the 2-hydroxyglutarate and isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenases as alternative electron donors linking lysine catabolism to the electron transport chain of Arabidopsis mitochondria
- PMID: 20501910
- PMCID: PMC2899879
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.110.075630
Identification of the 2-hydroxyglutarate and isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenases as alternative electron donors linking lysine catabolism to the electron transport chain of Arabidopsis mitochondria
Abstract
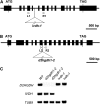
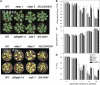
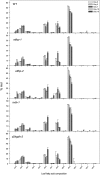
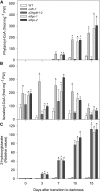
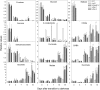
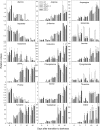
The process of dark-induced senescence in plants is relatively poorly understood, but a functional electron-transfer flavoprotein/electron-transfer flavoprotein:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETF/ETFQO) complex, which supports respiration during carbon starvation, has recently been identified. Here, we studied the responses of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants deficient in the expression of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase and 2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase to extended darkness and other environmental stresses. Evaluations of the mutant phenotypes following carbon starvation induced by extended darkness identify similarities to those exhibited by mutants of the ETF/ETFQO complex. Metabolic profiling and isotope tracer experimentation revealed that isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase is involved in degradation of the branched-chain amino acids, phytol, and Lys, while 2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase is involved exclusively in Lys degradation. These results suggest that isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase is the more critical for alternative respiration and that a series of enzymes, including 2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, plays a role in Lys degradation. Both physiological and metabolic phenotypes of the isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase and 2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase mutants were not as severe as those observed for mutants of the ETF/ETFQO complex, indicating some functional redundancy of the enzymes within the process. Our results aid in the elucidation of the pathway of plant Lys catabolism and demonstrate that both isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase and 2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase act as electron donors to the ubiquinol pool via an ETF/ETFQO-mediated route.
Figures



References
-
- Azevedo R.A., Arruda P. (April 7, 2010). High-lysine maize: the key discoveries that have made it possible. Amino Acids, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0576-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Azevedo R.A., Lea P.J. (2001). Lysine metabolism in higher plants. Amino Acids 20: 261–279 - PubMed
-
- Beckmann J.D., Frerman F.E. (1985). Electron-transfer flavoprotein:ubiquinone oxidoreductase from pig liver: Purification and molecular, redox, and catalytic properties. Biochemistry 24: 3913–3921 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

