Controlling the fate of NIK: a central stage in noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling
- PMID: 20501935
- PMCID: PMC5753754
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.3123pe18
Controlling the fate of NIK: a central stage in noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling
Abstract
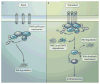
The noncanonical nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway is a specific arm of NF-kappaB signaling that regulates important aspects of immune function. Activation of this pathway centers on the modulation of a pivotal signaling component: NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK). Under normal conditions, NIK undergoes constitutive degradation, which keeps its abundance below the threshold required for its function, and signal-induced activation of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway is coupled with the stabilization and accumulation of NIK. A study now shows that signal-induced accumulation of NIK is subject to feedback control, which involves its phosphorylation by a downstream kinase, inhibitor of kappaB (IkappaB) kinase alpha (IKKalpha), and degradation. Thus, controlling the fate of NIK is emerging as a central mechanism in noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling.
Figures
Comment on
-
Negative feedback in noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling modulates NIK stability through IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation.Sci Signal. 2010 May 25;3(123):ra41. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000778. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20501937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:693–733. - PubMed
-
- Pasparakis M. Regulation of tissue homeostasis by NF-kappaB signalling: Implications for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:778–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

