Development of a cross-platform biomarker signature to detect renal transplant tolerance in humans
- PMID: 20501943
- PMCID: PMC2877932
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI39922
Development of a cross-platform biomarker signature to detect renal transplant tolerance in humans
Abstract
Identifying transplant recipients in whom immunological tolerance is established or is developing would allow an individually tailored approach to their posttransplantation management. In this study, we aimed to develop reliable and reproducible in vitro assays capable of detecting tolerance in renal transplant recipients. Several biomarkers and bioassays were screened on a training set that included 11 operationally tolerant renal transplant recipients, recipient groups following different immunosuppressive regimes, recipients undergoing chronic rejection, and healthy controls. Highly predictive assays were repeated on an independent test set that included 24 tolerant renal transplant recipients. Tolerant patients displayed an expansion of peripheral blood B and NK lymphocytes, fewer activated CD4+ T cells, a lack of donor-specific antibodies, donor-specific hyporesponsiveness of CD4+ T cells, and a high ratio of forkhead box P3 to alpha-1,2-mannosidase gene expression. Microarray analysis further revealed in tolerant recipients a bias toward differential expression of B cell-related genes and their associated molecular pathways. By combining these indices of tolerance as a cross-platform biomarker signature, we were able to identify tolerant recipients in both the training set and the test set. This study provides an immunological profile of the tolerant state that, with further validation, should inform and shape drug-weaning protocols in renal transplant recipients.
Figures
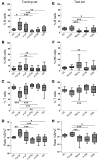
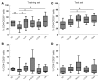
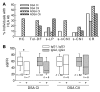
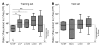
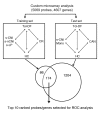
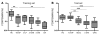

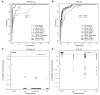
Comment in
-
Gazing into a crystal ball to predict kidney transplant outcome.J Clin Invest. 2010 Jun;120(6):1803-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI43286. Epub 2010 May 24. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20501950 Free PMC article.
-
Journal club. A B-cell signature associated with renal transplant tolerance in humans.Kidney Int. 2010 Sep;78(5):429. Kidney Int. 2010. PMID: 20734472 No abstract available.
References
-
- Owens ML, Maxwell JG, Goodnight J, Wolcott MW. Discontinuance of immunosuppression in renal transplant patients. Arch Surg. 1975;110(12):1450–1451. - PubMed
-
- Uehling DT, Hussey JL, Weinstein AB, Wank R, Bach FH. Cessation of immunosuppression after renal transplantation. Surgery. 1976;79(3):278–282. - PubMed
-
- Strober S, Benike C, Krishnaswamy S, Engleman EG, Grumet FC. Clinical transplantation tolerance twelve years after prospective withdrawal of immunosuppressive drugs: studies of chimerism and anti-donor reactivity. Transplantation. 2000;69(8):1549–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

