Factor V is an anticoagulant cofactor for activated protein C during inactivation of factor Va
- PMID: 20501981
- PMCID: PMC2974842
- DOI: 10.1159/000315141
Factor V is an anticoagulant cofactor for activated protein C during inactivation of factor Va
Abstract
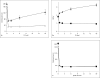
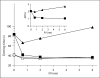
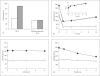
Coagulation factor V (FV) promotes inactivation of activated factor VIII (FVIIIa) by activated protein C (APC) and protein S. Loss of this APC cofactor activity is proposed to be partially responsible for the APC resistance phenotype of FV(Leiden). However, FVIIIa loses activity rapidly due to dissociation of the A2 domain, and this may be the primary mechanism of FVIIIa inactivation. APC/protein S also readily inactivates activated FV (FVa). We therefore hypothesized that FV can function as an anticoagulant cofactor for APC/protein S in the inactivation of FVa. FV was titrated into FV-deficient plasma, and the APC sensitivity ratio (APCsr; a measure of APC activity) was measured in a clotting assay that was not sensitive to FVIII. Our results showed an increase in APCsr as the FV concentration increased, suggesting an anticoagulant function for FV in this assay. FV(Leiden) showed APC resistance with an APCsr of 1.0. Therefore, under our experimental conditions, FV acted as an anticoagulant cofactor for APC in the inactivation of FVa.
Copyright © 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and functional characterization of a novel F5 mutation (Ala512Val, FVB onn ) associated with activated protein C resistance.J Thromb Haemost. 2016 Jul;14(7):1353-63. doi: 10.1111/jth.13339. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Thromb Haemost. 2016. PMID: 27090446
-
The C-terminal region of the factor V B-domain is crucial for the anticoagulant activity of factor V.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 26;273(26):16140-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.26.16140. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9632668
-
Comparison of activated protein C/protein S-mediated inactivation of human factor VIII and factor V.Blood. 1996 Jun 1;87(11):4708-17. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8639840
-
Factor V and thrombotic disease: description of a janus-faced protein.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002 Apr 1;22(4):530-8. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000012665.51263.b7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002. PMID: 11950687 Review.
-
The anticoagulant function of coagulation factor V.Thromb Haemost. 2012 Jan;107(1):15-21. doi: 10.1160/TH11-06-0431. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22116556 Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial cell dysfunction, coagulation, and angiogenesis in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Microvasc Res. 2021 Sep;137:104188. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104188. Epub 2021 May 20. Microvasc Res. 2021. PMID: 34022205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety, Stability and Pharmacokinetic Properties of (super)Factor Va, a Novel Engineered Coagulation Factor V for Treatment of Severe Bleeding.Pharm Res. 2016 Jun;33(6):1517-26. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-1895-3. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 26960296 Free PMC article.
-
Continuing education course #2: current understanding of hemostasis.Toxicol Pathol. 2011 Jan;39(1):273-80. doi: 10.1177/0192623310389474. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Toxicol Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21119054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function of the activated protein C (APC) autolysis loop in activated FVIII inactivation.Br J Haematol. 2011 Jun;153(5):644-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08657.x. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Br J Haematol. 2011. PMID: 21457218 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Regulatory Effects of Factor V Leiden and Factor V rs6028 in Breast Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 25;16(7):735. doi: 10.3390/genes16070735. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tracy PB, Eide LL, Bowie EJ, Mann KG. Radioimmunoassay of factor V in human plasma and platelets. Blood. 1982;60:59–63. - PubMed
-
- Shen L, Dahlback B. Factor V and protein S as synergistic cofactors to activated protein C in degradation of factor VIIIa. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:18735–18738. - PubMed
-
- Thorelli E, Kaufman RJ, Dahlback B. Cleavage of factor V at Arg 506 by activated protein C and the expression of anticoagulant activity of factor V. Blood. 1999;93:2552–2558. - PubMed
-
- Lu D, Kalafatis M, Mann KG, Long GL. Comparison of activated protein C/protein S-mediated inactivation of human factor VIII and factor V. Blood. 1996;87:4708–4717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

