Lack of support for association between the KIF1B rs10492972[C] variant and multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 20502484
- PMCID: PMC3109873
- DOI: 10.1038/ng0610-469
Lack of support for association between the KIF1B rs10492972[C] variant and multiple sclerosis
Figures
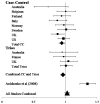
Comment on
-
Genetic variation in the KIF1B locus influences susceptibility to multiple sclerosis.Nat Genet. 2008 Dec;40(12):1402-3. doi: 10.1038/ng.251. Epub 2008 Nov 9. Nat Genet. 2008. PMID: 18997785
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

