Molecular recognition of organic ammonium ions in solution using synthetic receptors
- PMID: 20502608
- PMCID: PMC2874414
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.6.32
Molecular recognition of organic ammonium ions in solution using synthetic receptors
Abstract
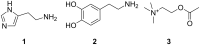
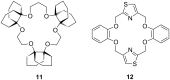
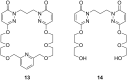
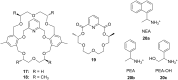
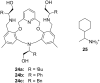
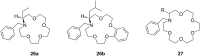
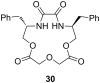
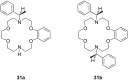
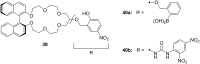
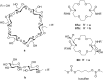
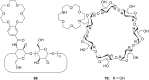
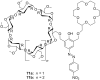
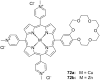
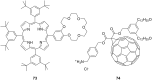
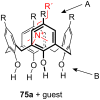
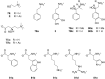
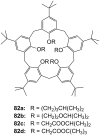
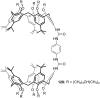
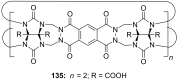
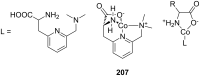
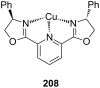
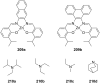
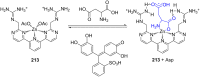
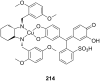
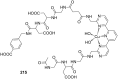
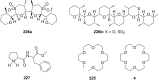
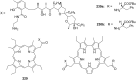
Ammonium ions are ubiquitous in chemistry and molecular biology. Considerable efforts have been undertaken to develop synthetic receptors for their selective molecular recognition. The type of host compounds for organic ammonium ion binding span a wide range from crown ethers to calixarenes to metal complexes. Typical intermolecular interactions are hydrogen bonds, electrostatic and cation-π interactions, hydrophobic interactions or reversible covalent bond formation. In this review we discuss the different classes of synthetic receptors for organic ammonium ion recognition and illustrate the scope and limitations of each class with selected examples from the recent literature. The molecular recognition of ammonium ions in amino acids is included and the enantioselective binding of chiral ammonium ions by synthetic receptors is also covered. In our conclusion we compare the strengths and weaknesses of the different types of ammonium ion receptors which may help to select the best approach for specific applications.
Keywords: amino acids; ammonium ion; molecular recognition; synthetic receptors.
Figures



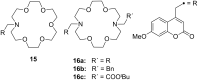



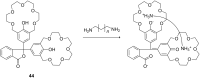





































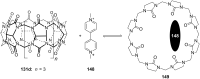


































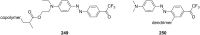
Similar articles
-
Solution- and gas-phase study of binding of ammonium and bisammonium hydrocarbons to oxacalix[4]arene carboxylate.RSC Adv. 2023 Jan 4;13(2):1041-1048. doi: 10.1039/d2ra07614d. eCollection 2023 Jan 3. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36686943 Free PMC article.
-
Stimuli-responsive host-guest systems based on the recognition of cryptands by organic guests.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Jul 15;47(7):1995-2005. doi: 10.1021/ar500046r. Epub 2014 May 8. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24804805
-
Hydrogen-bonding interactions in gas-phase polyether/ammonium ion complexes.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1994 Apr;5(4):260-73. doi: 10.1016/1044-0305(94)85016-X. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1994. PMID: 24222563
-
Proton transfer mediated recognition of amines by ionizable macrocyclic receptors.Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Sep 27;58(77):10743-10756. doi: 10.1039/d2cc04047f. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022. PMID: 36102659 Review.
-
Anion transport with halogen bonds.Top Curr Chem. 2015;358:205-39. doi: 10.1007/128_2014_541. Top Curr Chem. 2015. PMID: 24696354 Review.
Cited by
-
Making wastewater obsolete: Selective separations to enable circular water treatment.Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2021 Jan 6;5:100078. doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2021.100078. eCollection 2021 Jan. Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2021. PMID: 36158609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Landscape of Aptamers: From Cross-Reactive to Selective to Specific, High-Affinity Receptors for Cocaine.JACS Au. 2024 Feb 13;4(2):760-770. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00781. eCollection 2024 Feb 26. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 38425914 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and spectroscopic properties of crown ether-capped dibenzotetraaza[14]annulenes.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2019 Mar 11;15:617-622. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.15.57. eCollection 2019. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2019. PMID: 30931003 Free PMC article.
-
tert-Butyl N-(4-hy-droxy-benz-yl)-N-[4-(prop-2-yn-yloxy)benz-yl]carbamate.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Oct 1;67(Pt 10):o2642. doi: 10.1107/S160053681103683X. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 22058772 Free PMC article.
-
pH-Responsive chromogenic-sensing molecule based on bis(indolyl)methene for the highly selective recognition of aspartate and glutamate.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011 Feb 16;7:218-21. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.7.29. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 21448262 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
