Sequencing, analysis, and annotation of expressed sequence tags for Camelus dromedarius
- PMID: 20502665
- PMCID: PMC2873428
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010720
Sequencing, analysis, and annotation of expressed sequence tags for Camelus dromedarius
Abstract
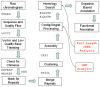
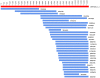
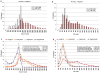
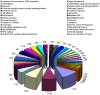
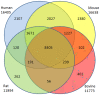
Despite its economical, cultural, and biological importance, there has not been a large scale sequencing project to date for Camelus dromedarius. With the goal of sequencing complete DNA of the organism, we first established and sequenced camel EST libraries, generating 70,272 reads. Following trimming, chimera check, repeat masking, cluster and assembly, we obtained 23,602 putative gene sequences, out of which over 4,500 potentially novel or fast evolving gene sequences do not carry any homology to other available genomes. Functional annotation of sequences with similarities in nucleotide and protein databases has been obtained using Gene Ontology classification. Comparison to available full length cDNA sequences and Open Reading Frame (ORF) analysis of camel sequences that exhibit homology to known genes show more than 80% of the contigs with an ORF>300 bp and approximately 40% hits extending to the start codons of full length cDNAs suggesting successful characterization of camel genes. Similarity analyses are done separately for different organisms including human, mouse, bovine, and rat. Accompanying web portal, CAGBASE (http://camel.kacst.edu.sa/), hosts a relational database containing annotated EST sequences and analysis tools with possibility to add sequences from public domain. We anticipate our results to provide a home base for genomic studies of camel and other comparative studies enabling a starting point for whole genome sequencing of the organism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Al-Swailem AM, Al-Busadah KA, Shehata MM, Al-Anazi IO, Askari E. Classification of Saudi Arabian camel (Camelus dromedarius) subtypes based on RAPD technique. Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment. 2007;5:143–148.
-
- Emmanuel B, Nahapetian A. Fatty acid composition of depot fats and rumen wall of the camel (Camelus dromedarius). Comparative Biochemistry Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 1980;67:701–704.
-
- Duncan WRH, Garton GA. The fatty acid composition and intermolecular structure of triglycerides derived from different sites in the body of the sheep. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 1967;18:99–102. - PubMed
-
- Al-Ani FK. Camel management and diseases. Amman, Jordan: Al-Shraq Printing Press & Dar Ammar Book Publishing; 2004.
-
- Muyldermans S. Single domain camel antibodies: current status. J Biotechnol. 2001;74:277–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

